Microbes, infections, diet, environmental exposures, and genetics influence how the immune system functions and the likelihood that a person will develop autoimmunity. Understanding the influences of these factors, among others, may enable scientists to modify them to prevent or treat autoimmune disease.
The Microbiome
Trillions of microscopic organisms collectively called the human microbiome live on and in the human body. Many of these organisms coevolved with people and have beneficial functions, including aiding immune system development. Changes to the balance and diversity of the microbiome can lead to immune disruption and disease, from infections to inflammation to autoimmunity.
Diet
Since diet is one of many factors that influence the composition of the microbiome, researchers are studying the impact of diet on autoimmunity and immune health.
Genetics
Genetics also play a role in autoimmunity. Genetic variants (mutations) normally present in the human population can affect immune processes and thereby influence susceptibility to infections and autoimmune diseases. Identifying these variants and uncovering how they impact the immune response may help scientists understand how the variants contribute to the development of autoimmune disease.
Scientists Discover Cause, Potential Treatment for Cases of Deadly Autoimmune Disorder
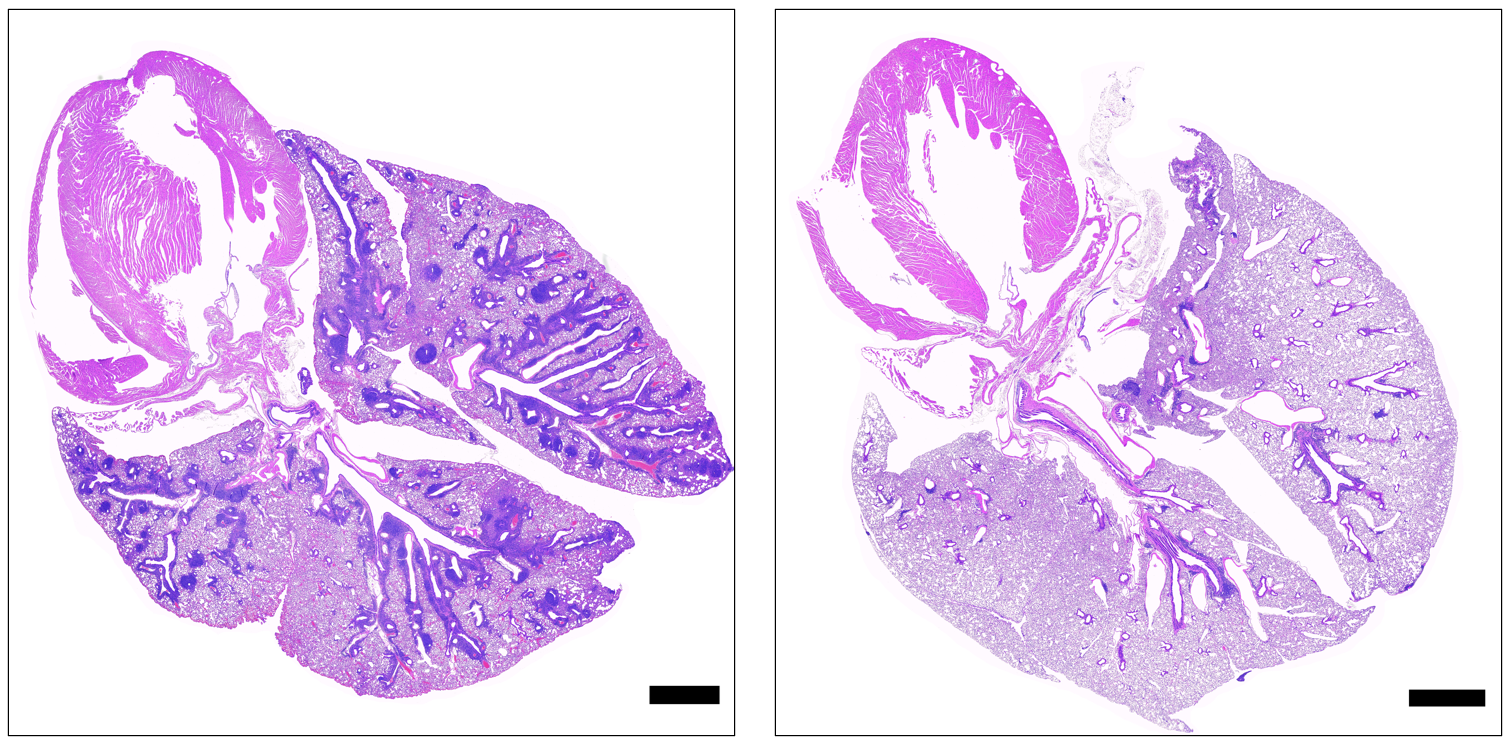
November 6, 2024Discovery of a gene variant causing some cases of APECED, a rare inherited autoimmune disease, will enable earlier diagnosis & medical care that may prolong lives.
Existing Drug Shows Promise as Treatment for Rare Genetic Disorder
May 30, 2024A drug approved to treat certain autoimmune diseases and cancers successfully alleviated symptoms of a rare genetic syndrome called autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1 (APS-1).