Through the NIAID Preclinical Services Program, researchers are evaluating compounds for antiviral activity against a panel of viruses, including West Nile virus (WNV). In 2011 and 2012, nine compounds were tested for activity against WNV in rodent models of disease, and 220 compounds were tested in vitro (in cell culture). Promising compounds will be further analyzed for safety and efficacy.
In 2011 and 2012, NIAID awarded six research grants to scientists studying small-molecular-weight compounds as potential antivirals to treat flaviviruses, including WNV. Other therapeutic approaches that are being investigated include
- Monoclonal antibodies that target WNV particles to inhibit spread of infection
- Monoclonal antibodies to target and destroy WNV-infected cells
- Broad-spectrum therapeutics for flaviviruses, including WNV
- Therapeutics that are able to cross the blood-brain barrier
- Identification of drug targets for viruses that infect the nervous system
Development of broad-spectrum immunotherapeutics, such as monoclonal antibodies or bi-specific antibodies, that target specific viral pathways.
Scientific Advances
COVID-19 Respiratory Treatment Effective in Encephalitis Study
October 1, 2024Antiviral drug molnupiravir, a COVID-19 treatment, was effective when tested in mice in preventing viruses that cause brain swelling, particularly in children. The scientists studied LACV because it broadly represents several RNA viruses that cause disease in the CNS, including Jamestown Canyon and Cache Valley viruses – which also were part of the study – and rabies, polio, West Nile, Nipah and…
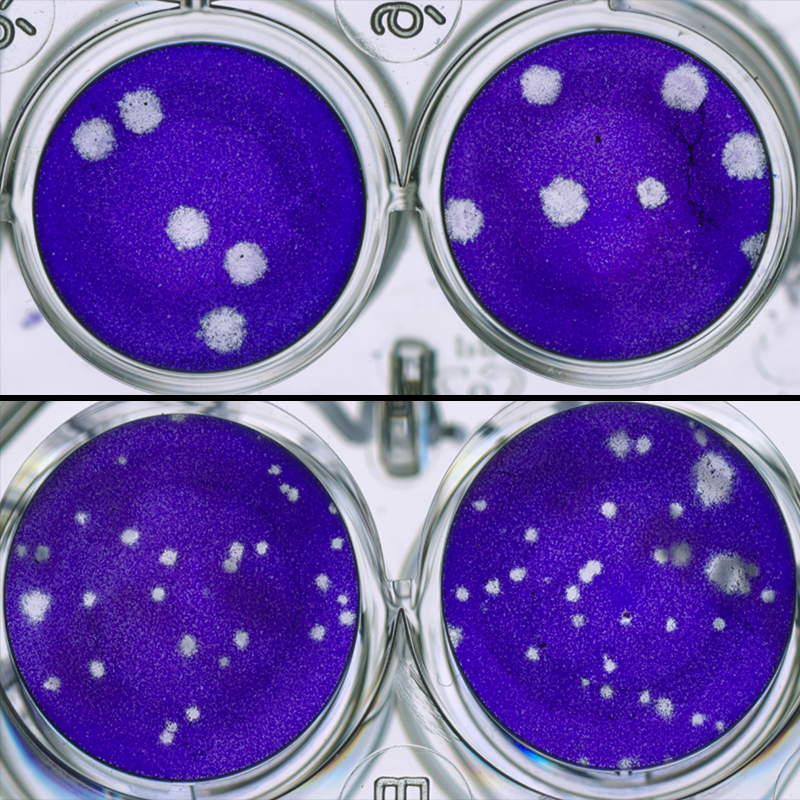
Promising Advances for Antibody Treatment of Viruses that Cause Neurologic and Arthritic Diseases
June 9, 2023NIAID scientists and colleagues are one step closer to developing a safe and effective therapy against alphaviruses, which are spread by mosquitoes and can cause two types of disease in people: causing severe neurological impairment such as encephalitis (brain swelling) or crippling muscle pain similar to arthritis.



