42 Results
Powerful Sequencing Tool Helps Identify Infectious Diseases in Mali
Advanced diagnostic tool tested in Mali helped identify infectious viruses in patients that normally would have required many traditional tests.

Vaccine Protective Against H5N1 Influenza from Cattle
Experimental H5N1 vaccine fully protective in mice against virus circulating in U.S. cattle.
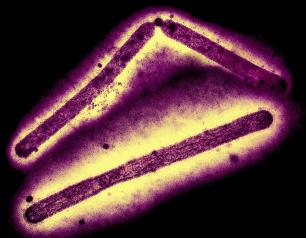
Subclinical Disease in Monkeys Exposed to H5N1 by Mouth and Stomach
Drinking raw milk contaminated with H5N1 virus can cause infection but may be less severe. Regardless, exposure by raw milk should be avoided.
Measuring Innovation: Laboratory Infrastructure to Deliver Essential HIV Clinical Trial Results
HIV clinical trials network laboratory functions will continue to evolve to align with scientific priorities and research approaches.
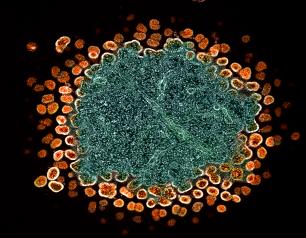
Shaping the Next Era of HIV Therapeutics and Care
The Institute aims to foster the next generation of discoveries that will enable people with HIV to experience a typical lifespan with high life quality. Scientific priorities include removing the chronic HIV medication burden; reducing the incidence of concurrent TB and hepatitis; and ensuring scientific advances can feasibly be scaled to all who stand to benefit.
Gene Signature at Birth Predicts Sepsis in Newborns Before Signs Appear
A four-gene signature in newborns’ blood at birth predicts before symptom onset whether a baby will develop neonatal sepsis during the first week of life.

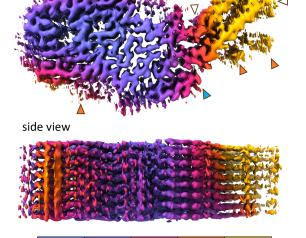
NIAID Scientists Detail First Structure of a Natural Mammalian Prion
Revealing the near-atomic structure of a chronic wasting disease prion from a deer should help scientists explain how CWD prions spread and become infectious.
COVID-19 Respiratory Treatment Effective in Encephalitis Study
Antiviral drug molnupiravir, a COVID-19 treatment, was effective when tested in mice in preventing viruses that cause brain swelling, particularly in children. The scientists studied LACV because it broadly represents several RNA viruses that cause disease in the CNS, including Jamestown Canyon and Cache Valley viruses – which also were part of the study – and rabies, polio, West Nile, Nipah and several other viruses not part of the study.
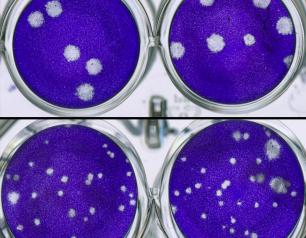
The Eyes Have it: A Functional Role for Prion Protein
Answers to what a normal prion protein does could help lead them to develop treatments and disease-prevention measures against human prion diseases, such as Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, fatal familial insomnia and kuru, as well as animal prion diseases, such as scrapie in sheep and chronic wasting disease in cervids.
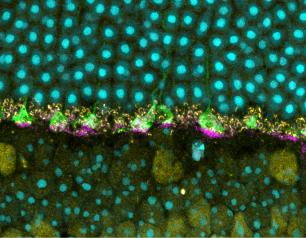
Study Links Certain Vaginal Bacteria and Inflammatory Marker to Increased Odds of Acquiring HIV Among Cisgender Women
Fourteen vaginal bacterial species and the presence of a protein that promotes inflammation were associated with increased odds of HIV acquisition in a study of more than 500 cisgender women in African countries with high HIV incidence. The study was the largest to date to prospectively analyze the relationship between both the vaginal microbiome and vaginal tissue inflammation and the likelihood of acquiring HIV among cisgender women in this population.
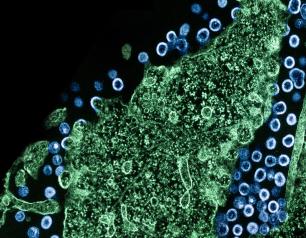
Bringing HIV Study Protocols to Life with Representative, High-Quality Research
The HIV clinical trials network sites have made tremendous contributions to NIH’s scientific priorities by offering direct access to and consultation with populations most affected by HIV globally, and by delivering high-quality clinical research with strong connections to trusted community outreach platforms. Future networks will need to maintain core strengths of current models while expanding capacity in areas vital to further scientific progress. These include operations that inform pandemic responses and extending our reach within communities impacted by HIV, including populations historically underrepresented in clinical research.
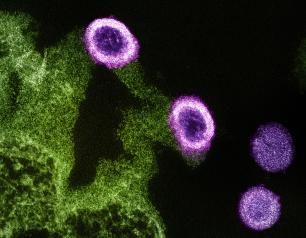
Charting the Path to an HIV-Free Generation
NIAID supports four research networks as part of its HIV clinical research enterprise. Every seven years, the Institute engages research partners, community representatives, and other public health stakeholders in a multidisciplinary evaluation of network progress toward short- and long-term scientific goals. Pregnancy, childbirth and the postnatal period are a key focus of NIAID HIV research and call for measures to support the health of people who could become pregnant as well as their infants.
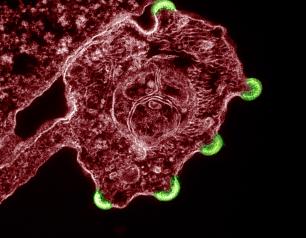
Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies Evaluated in Many HIV Cure Strategies
Many promising HIV cure strategies use broadly neutralizing antibodies, or bNAbs, which can neutralize a wide range of HIV variants, homing in on and binding to specific viral components, and then acting to destroy the virus by triggering an immune response. Several HIV bNAbs have been developed and tested to determine whether they can prevent or treat HIV. NIAID and partners are evaluating bNAb-based strategies alone and in combination with other immunity-enhancing strategies for HIV clearance in clinical trials in in Africa, North and South America, and Southeast Asia.

AIDS 2024: Research Updates, HIV Criminalization Laws, and AI (VIDEO)
HIV.gov continued daily coverage of AIDS 2024. This blog post includes recaps of four livestreamed conversations.

Stepping into Science
Realizing that traditional laboratory science – aka “bench research” – isn’t for everyone, staff at NIAID's Rocky Mountain Laboratories recently invited two dozen area high school students to experience not only traditional research but also the lesser-known careers that make bench research possible.
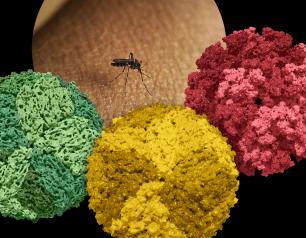
NIAID Raises Awareness to Malaria-like Diseases in W. Africa
NIAID scientists and colleagues have identified dengue, Zika and chikungunya viruses in the West African country of Mali, where health care providers could be misdiagnosing patients as having malaria. All four infectious diseases are caused by a mosquito bite.
NIAID Research Team Develops 2nd Model of Crimean-Congo Fever
A NIAID research team has developed an additional nonhuman primate study model for Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever (CCHF), providing an alternative for development of critically needed vaccines and therapeutics.
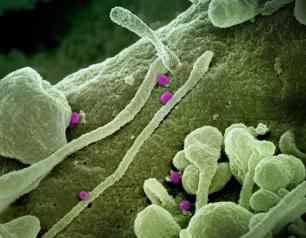
NIAID Targets Transport System as Lyme Disease Treatment
NIAID scientists and colleagues are investigating a potential treatment strategy against Lyme disease that would directly suppress Borrelia burgdorferi, the bacterium that causes the disease.
NIAID Marks HIV Vaccine Awareness Day 2024
On the 27th observance of HIV Vaccine Awareness Day (Saturday, May 18), we express our gratitude to the dedicated global community of scientists, advocates, study participants, study staff, and funders working toward a safe, effective, durable, and accessible HIV vaccine.
New Tool Identifies Aedes Mosquito Exposure in People
Scientists at NIAID developed a new tool to help identify geographic hot spots for Aedes mosquitoes, a type of mosquito that can spread diseases such as dengue, Zika and chikungunya. The tool uses a marker from blood serum to identify people bitten by Aedes mosquitoes. Monitoring for this marker in blood samples could help find sites where disease-carrying mosquitoes live, allowing for targeted interventions against dengue and other diseases.
Experimental Ebola Vaccines Found Safe and Capable of Producing Immune Responses in Healthy Adults
Ebola viruses cause devastating disease in people, resulting in severe and often fatal hemorrhagic fever called Ebola virus disease. Of the four species of Ebola viruses that cause disease in people, Zaire ebolavirus (EBOV) and Sudan ebolavirus (SUDV) have caused more than 30 known outbreaks in the last century, killing more than half of those with the disease. Scientists at NIAID’s Vaccine Research Center (VRC) developed novel vaccines to combat these viruses, which were advanced to clinical trials in response to the 2014-2016 Ebola epidemic in the West African countries of Guinea, Liberia, and Sierra Leone. In two phase 1/1b trials conducted in the United States and Uganda, the researchers evaluated combinations of the experimental vaccines against Ebola disease in healthy adults, finding them safe, tolerable, and capable of producing immune responses. Comparisons between the different vaccine regimens revealed important data on how the vaccines could be administered in routine and outbreak settings. The results of the trials were published last week in npj Vaccines.
A Change in Drug Regimen is Associated with Temporary Increases in Dormant HIV
Switching to an antiretroviral therapy (ART) regimen containing the drug dolutegravir was associated with a significant temporary increase in reservoirs of latent HIV, according to a new analysis from a study in Uganda. HIV reservoirs are cells where HIV lies dormant and cannot be reached by the immune system or ART. They are central to HIV’s persistence, preventing current treatments from clearing the virus from the body.
Doxy-PEP, HIV Vaccines and Community-Engaged Research: Discussions with Carl Dieffenbach and LaRon Nelson at CROI 2024 (VIDEO)
During the first full day of presentations at the 2024 Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections, HIV.gov spoke with Carl Dieffenbach, Ph.D., director of NIAID’s Division of AIDS, and LaRon Nelson, Ph.D., R.N., F.N.P., F.N.A.P., F.N.Y.A.M., F.A.A., professor and associate dean at the Yale School of Nursing. They discussed Doxy-PEP for STI prevention, HIV vaccines, community engagement in research, and more. Watch their discussions.

New Guidelines for Use of Statins by People with HIV to Prevent Cardiovascular Events
The Department of Health and Human Services Guidelines Panel for the Use of Antiretroviral Agents in Adults and Adolescents with HIV (the Panel) has developed recommendations for the use of statin therapy in people with HIV, in collaboration with representatives from the American College of Cardiology, the American Heart Association, and the HIV Medicine Association.

NIAID and Cuban Scientists Gather to Discuss Global Health Challenges
Recent disease outbreaks in the Americas led U.S. and Cuban scientists to hold a meeting Feb. 14-16 on Addressing Global Health Challenges Through Scientific Innovation and Biomedical Research.


