35 Results
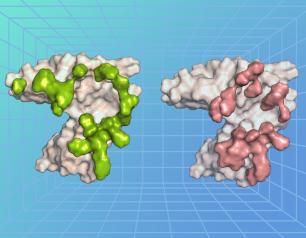
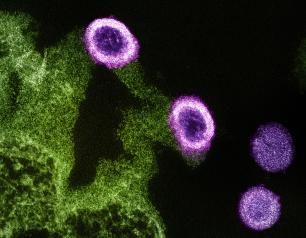
Epstein-Barr Virus’s Molecular Mimicry Reveals a Key Site of Vulnerability
NIAID scientists determined the high-resolution 3D structure of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) surface protein in complex with its receptor, revealing a key site of vulnerability that could lead to much-needed interventions against this common human pathogen.
Vaccine Protective Against H5N1 Influenza from Cattle
Experimental H5N1 vaccine fully protective in mice against virus circulating in U.S. cattle.
Subclinical Disease in Monkeys Exposed to H5N1 by Mouth and Stomach
Drinking raw milk contaminated with H5N1 virus can cause infection but may be less severe. Regardless, exposure by raw milk should be avoided.
Measuring Innovation: Laboratory Infrastructure to Deliver Essential HIV Clinical Trial Results
HIV clinical trials network laboratory functions will continue to evolve to align with scientific priorities and research approaches.
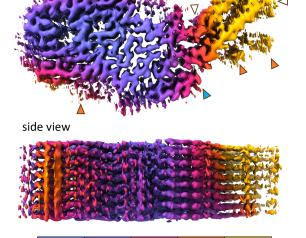
NIAID Scientists Detail First Structure of a Natural Mammalian Prion
Revealing the near-atomic structure of a chronic wasting disease prion from a deer should help scientists explain how CWD prions spread and become infectious.
HIVR4P 2024 Research Highlights: Reproductive Health While on PrEP and Signals to Guide HIV Vaccines and Cure
New NIAID-supported science presented at the 2024 HIV Research for Prevention conference in Lima, Peru features a breadth of HIV discovery and translational findings and enriches the evidence base on HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis within the context of reproductive health.
Defining the Goals of HIV Science Through 2034
Discovery, Development and Delivery for an Increasingly Interconnected HIV Landscape
By Carl Dieffenbach, Ph.D., director, Division of AIDS, NIAID
We envision an HIV research enterprise that follows a logical evolution in addressing new scientific priorities informed by previous research progress. We will fund our next networks to align with updated research goals to take us through the end of 2034. Our capacity must reflect an increasing interdependence across clinical practice areas and public health contexts.
Bringing HIV Study Protocols to Life with Representative, High-Quality Research
The HIV clinical trials network sites have made tremendous contributions to NIH’s scientific priorities by offering direct access to and consultation with populations most affected by HIV globally, and by delivering high-quality clinical research with strong connections to trusted community outreach platforms. Future networks will need to maintain core strengths of current models while expanding capacity in areas vital to further scientific progress. These include operations that inform pandemic responses and extending our reach within communities impacted by HIV, including populations historically underrepresented in clinical research.
Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies Evaluated in Many HIV Cure Strategies
Many promising HIV cure strategies use broadly neutralizing antibodies, or bNAbs, which can neutralize a wide range of HIV variants, homing in on and binding to specific viral components, and then acting to destroy the virus by triggering an immune response. Several HIV bNAbs have been developed and tested to determine whether they can prevent or treat HIV. NIAID and partners are evaluating bNAb-based strategies alone and in combination with other immunity-enhancing strategies for HIV clearance in clinical trials in in Africa, North and South America, and Southeast Asia.

NIAID Research to Eliminate the Threat of Viral Hepatitis Across the Globe
Viral hepatitis affects the lives of about one in twenty people in the world, resulting in over a million deaths each year. NIAID is working on many ways to prevent and treat the different types of hepatitis, including the development of vaccines and improved therapeutics and diagnostics. July 28 is observed annually as World Hepatitis Day, providing an opportunity to reflect on the impact of hepatitis on global health and focus on strategies to reduce its burden. To observe World Hepatitis Day, NIAID highlights recent advancements researchers have made in these areas.
AIDS 2024: Long-Acting Injectables, Bi-Directional Learning, PACHA & More (VIDEO)
HIV.gov continued daily coverage of AIDS 2024. Tune in to four conversations livestreamed at the conference.
AIDS 2024: NIH Research Updates, Inequities, U=U, and Doxy PrEP (VIDEO)
The AIDS 2024 conference is taking place in Munich, Germany. HIV.gov is providing daily coverage.

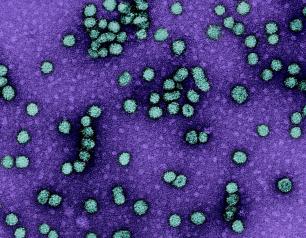
NIAID Research Team Develops 2nd Model of Crimean-Congo Fever
A NIAID research team has developed an additional nonhuman primate study model for Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever (CCHF), providing an alternative for development of critically needed vaccines and therapeutics.
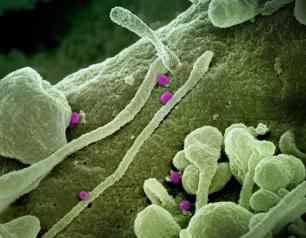
Proof-of-Concept Study Shows an HIV Vaccine Can Generate Key Antibody Response in People
An HIV vaccine candidate elicited trace levels of HIV broadly neutralizing antibodies and high levels of other key immune cells in an early-stage clinical trial. This immune response is an important signal that, if antibody levels can be further amplified, the vaccination strategy might be able to prevent HIV.
NIAID Marks HIV Vaccine Awareness Day 2024
On the 27th observance of HIV Vaccine Awareness Day (Saturday, May 18), we express our gratitude to the dedicated global community of scientists, advocates, study participants, study staff, and funders working toward a safe, effective, durable, and accessible HIV vaccine.
Exploring a Meningitis Vaccine for Gonorrhea Prevention
A preventive vaccine for gonorrhea would be a major advance in public health, according to an editorial co-authored by NIAID Director Jeanne Marrazzo. The genetic sequences of the bacteria that cause gonorrhea and meningitis B, are closely related. This has led researchers to explore whether the 4CMenB vaccine, approved by the Food and Drug Administration for meningitis B, might also prevent gonorrhea. NIAID is sponsoring an efficacy study of the 4CMenB vaccine for gonorrhea prevention.
The HIV Field Needs Early-Stage Investigators (VIDEO)
by Jeanne Marrazzo, M.D., M.P.H., NIAID Director
The HIV research community is led by scientists with deep personal commitments to improving the lives of people with and affected by HIV. Our collective decades of work have generated HIV testing, prevention and treatment options beyond what we could have imagined in the 1980s. Those advances enable NIAID to explore new frontiers: expanding HIV prevention and treatment modalities, increasing understanding of the interplay between HIV and other infectious and non-communicable diseases, optimizing choice and convenience, and building on the ever-growing knowledge base that we need to develop a preventive vaccine and cure. The next generation of leaders will bring these concepts to fruition, and we need to welcome and support them into the complex and competitive field of HIV science.
Sexually Transmitted Infections—A Closer Look at NIAID Research
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites. NIAID supports research across the spectrum from basic to clinical science to develop effective diagnostic, preventive and therapeutic approaches to STIs in alignment with the National STI Strategic Plan. In recognition of National STI Awareness Week, NIAID shares a snapshot of new projects and recent scientific advances in STI research.
Experimental Ebola Vaccines Found Safe and Capable of Producing Immune Responses in Healthy Adults
Ebola viruses cause devastating disease in people, resulting in severe and often fatal hemorrhagic fever called Ebola virus disease. Of the four species of Ebola viruses that cause disease in people, Zaire ebolavirus (EBOV) and Sudan ebolavirus (SUDV) have caused more than 30 known outbreaks in the last century, killing more than half of those with the disease. Scientists at NIAID’s Vaccine Research Center (VRC) developed novel vaccines to combat these viruses, which were advanced to clinical trials in response to the 2014-2016 Ebola epidemic in the West African countries of Guinea, Liberia, and Sierra Leone. In two phase 1/1b trials conducted in the United States and Uganda, the researchers evaluated combinations of the experimental vaccines against Ebola disease in healthy adults, finding them safe, tolerable, and capable of producing immune responses. Comparisons between the different vaccine regimens revealed important data on how the vaccines could be administered in routine and outbreak settings. The results of the trials were published last week in npj Vaccines.
Promising Outcomes with HIV Treatment Started Promptly After Birth: Deborah Persaud Presents at CROI 2024 (VIDEO)
On the final day of the 2024 Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI), HIV.gov spoke with Deborah Persaud, M.D., professor of Pediatrics at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and director of the Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases at Johns Hopkins Children's Center, who reported findings from a study about whether very early initiation of antiretroviral therapy (ART) may limit the establishment of HIV reservoirs in newborns, potentially enabling ART-free remission. Dr. Persaud spoke with Catey Laube of NIAID's Office of Communications and Government Relations. Watch their conversation.

Doxy-PEP, HIV Vaccines and Community-Engaged Research: Discussions with Carl Dieffenbach and LaRon Nelson at CROI 2024 (VIDEO)
During the first full day of presentations at the 2024 Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections, HIV.gov spoke with Carl Dieffenbach, Ph.D., director of NIAID’s Division of AIDS, and LaRon Nelson, Ph.D., R.N., F.N.P., F.N.A.P., F.N.Y.A.M., F.A.A., professor and associate dean at the Yale School of Nursing. They discussed Doxy-PEP for STI prevention, HIV vaccines, community engagement in research, and more. Watch their discussions.

Novel CMV Vaccine Generates Stronger Response in Key Immune Cells Than Previous Candidate
A messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccine designed to prevent human cytomegalovirus (CMV) elicited long-lasting CMV-specific responses from several types of immune cells, outperforming a previous vaccine concept in multiple measures in a NIAID-supported laboratory study. The findings were published in the Journal of Infectious Diseases.
Antibodies Passed through Placenta May Improve Survival for Infants with HIV
Certain antibodies that pass through the placenta are associated with the improved survival of infants who acquire HIV through nursing. A Kenya-based study observed that preexisting antibodies that target a region of a protein on HIV's surface were correlated with delayed HIV acquisition in infants exposed to the virus as well as a lower amount of virus circulating in the blood of infants who acquired HIV.
The STOMP Trial Evaluates an Antiviral for Mpox
NIAID launched the STOMP trial to determine whether the antiviral drug tecovirimat can safely and effectively treat mpox. In a video, Dr. Cyrus Javan of NIAID's Division of AIDS explains the importance of the STOMP trial.
Building a Better Malaria Vaccine—NIAID Researchers Design a Paradigm-Busting Candidate
NIAID researchers used structural information about two malaria parasite proteins along with mechanistic information about the interaction between them to design and build an entirely novel candidate vaccine. When tested in rats, their “structure-based design 1” (SBD1) immunogen vaccine performed better than other experimental malaria vaccines. It also upends the conventional wisdom that successful vaccines must elicit receptor-blocking antibodies.