71 Results
NIAID Research Key to H5N1 Influenza Preparedness Efforts
H5N1 influenza viruses have been around for years, but the spring 2024 outbreak of a highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza among U.S. dairy cows prompted new concerns. NIAID scientists and NIAID-funded researchers have been working closely to monitor the outbreak, understand spread among animals and develop potential prevention and treatment methods as part of larger U.S. government pandemic preparedness efforts.

Calling for Reinforcements: A New Way to Recruit Immune System Helpers Could Lead to Better Flu Vaccines
Flu causes hundreds of thousands of deaths and millions of hospitalizations worldwide. The best way to protect against serious illness is annual vaccination, but the vaccine’s effectiveness is not perfect. Now, NIH-funded researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine have taken a new approach to crafting flu vaccines that resulted, in lab tests, in a more broadly protective immune response compared to currently available vaccines.
Some People with Advanced HIV Have Anti-CD4 Autoantibodies Associated with Dampened Immune Recovery
A NIAID-sponsored analysis found that people with advanced HIV and anti-CD4 autoantibodies experienced limited CD4+ T-cell reconstitution through up to four years of observation after ART initiation, highlighting a potential immune effect of long-term unsuppressed HIV. The findings were published in Clinical Infectious Diseases.
Next-generation Genetic Tools Reveal New Aspects of Enterovirus Evolution
NIAID scientists developed tools to study evolution in enteroviruses—a virus group responsible for polio; hand, foot & mouth disease (HFMD); acute flaccid myelitis (AFM) & other diseases. Their findings may reveal pathways of viral evolution.
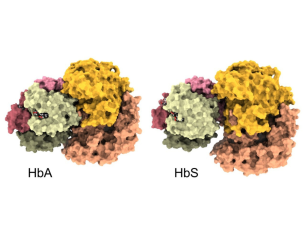
A New View of Hemoglobin and its Role in Malaria
A look inside human arteries reveals a new picture of hemoglobin’s role there and may lead to treatments for malaria and other vascular diseases.
First Webinar of Long COVID Treatment Initiative Highlights Early Progress
NIAID and the Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (FNIH) launched its first in a series of online webinars highlighting recent progress in the new Researching COVID to Enhance Recovery - Treating Long COVID (RECOVER-TLC) program.
New Resource for Researchers: NIH BioArt Source, a Free Science and Biomedical Art Resource Library
NIAID has launched a free science and biomedical art resource library created by professional medical illustrators. This open-source library offers a diverse array of high-quality illustrations to elevate the impact and clarity of scientific communications.

Scientists Discover Cause, Potential Treatment for Cases of Deadly Autoimmune Disorder
Discovery of a gene variant causing some cases of APECED, a rare inherited autoimmune disease, will enable earlier diagnosis & medical care that may prolong lives.
Shaping the Next Era of HIV Therapeutics and Care
The Institute aims to foster the next generation of discoveries that will enable people with HIV to experience a typical lifespan with high life quality. Scientific priorities include removing the chronic HIV medication burden; reducing the incidence of concurrent TB and hepatitis; and ensuring scientific advances can feasibly be scaled to all who stand to benefit.
Gene Signature at Birth Predicts Sepsis in Newborns Before Signs Appear
A four-gene signature in newborns’ blood at birth predicts before symptom onset whether a baby will develop neonatal sepsis during the first week of life.

Can Improved Tests Speed Up Treatment for Antibacterial Resistant Infections?
An ongoing NIAID-supported trial is testing whether rapid tests for antibiotic susceptibility can improve patient outcomes.
NIAID Scientists Detail First Structure of a Natural Mammalian Prion
Revealing the near-atomic structure of a chronic wasting disease prion from a deer should help scientists explain how CWD prions spread and become infectious.
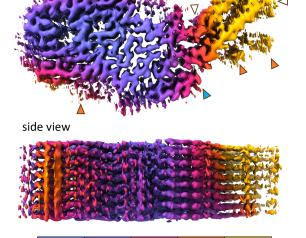
Sequencing of Congo Mpox Reports Highlights New Transmission Patterns in Country
Laboratory analysis in the Republic of Congo showed mpox was affecting people in parts of the country where it has not been historically. The findings point to increases in human-to-human transmission across the border with the neighboring Democratic Republic of the Congo, where a large outbreak was declared a public health emergency of international concern.
HIVR4P 2024 Research Highlights: Reproductive Health While on PrEP and Signals to Guide HIV Vaccines and Cure
New NIAID-supported science presented at the 2024 HIV Research for Prevention conference in Lima, Peru features a breadth of HIV discovery and translational findings and enriches the evidence base on HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis within the context of reproductive health.
COVID-19 Respiratory Treatment Effective in Encephalitis Study
Antiviral drug molnupiravir, a COVID-19 treatment, was effective when tested in mice in preventing viruses that cause brain swelling, particularly in children. The scientists studied LACV because it broadly represents several RNA viruses that cause disease in the CNS, including Jamestown Canyon and Cache Valley viruses – which also were part of the study – and rabies, polio, West Nile, Nipah and several other viruses not part of the study.
Defining the Goals of HIV Science Through 2034
Discovery, Development and Delivery for an Increasingly Interconnected HIV Landscape
By Carl Dieffenbach, Ph.D., director, Division of AIDS, NIAID
We envision an HIV research enterprise that follows a logical evolution in addressing new scientific priorities informed by previous research progress. We will fund our next networks to align with updated research goals to take us through the end of 2034. Our capacity must reflect an increasing interdependence across clinical practice areas and public health contexts.
The Eyes Have it: A Functional Role for Prion Protein
Answers to what a normal prion protein does could help lead them to develop treatments and disease-prevention measures against human prion diseases, such as Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, fatal familial insomnia and kuru, as well as animal prion diseases, such as scrapie in sheep and chronic wasting disease in cervids.
Fungal Disease Awareness Week—Fighting Fungi at NIAID
Fungal Disease Awareness Week spotlights clinical trials of improved treatments for fungal infections, such as better use of antibiotics and treatment combinations.
Study Links Certain Vaginal Bacteria and Inflammatory Marker to Increased Odds of Acquiring HIV Among Cisgender Women
Fourteen vaginal bacterial species and the presence of a protein that promotes inflammation were associated with increased odds of HIV acquisition in a study of more than 500 cisgender women in African countries with high HIV incidence. The study was the largest to date to prospectively analyze the relationship between both the vaginal microbiome and vaginal tissue inflammation and the likelihood of acquiring HIV among cisgender women in this population.
SARS-CoV-2 Rapidly Evolves in People with Advanced HIV
A NIAID study revealed how some variants of SARS-CoV-2—the virus that causes COVID-19—could evolve. The researchers used cutting-edge technology to examine genes from SARS-CoV-2 in people with and without HIV who also had COVID-19, looking at the different copies of the virus in individuals over time. They found that people with advanced HIV—as defined by reduced numbers of immune cells called CD4+ T cells—had dozens of SARS-CoV-2 variants in their bodies, compared to just one major variant in most people without HIV and people with HIV who had higher numbers of CD4+ T cells.
Bringing HIV Study Protocols to Life with Representative, High-Quality Research
The HIV clinical trials network sites have made tremendous contributions to NIH’s scientific priorities by offering direct access to and consultation with populations most affected by HIV globally, and by delivering high-quality clinical research with strong connections to trusted community outreach platforms. Future networks will need to maintain core strengths of current models while expanding capacity in areas vital to further scientific progress. These include operations that inform pandemic responses and extending our reach within communities impacted by HIV, including populations historically underrepresented in clinical research.
World Mosquito Day 2024—The Metabolic Mysteries of Mosquito Metabolism
Mosquitoes are considered one of the most dangerous animals on earth because of their broad distribution and the many pathogens they transmit to humans. Dr. Patricia Scaraffia, Associate Professor at the Tulane University School of Public Health and Tropical Medicine, has dedicated her career to understanding the metabolism of the mosquito species that carries the pathogens responsible for dengue, Zika, chikungunya, and yellow fever to humans. NIAID reached out to Dr. Scaraffia about her team’s research.

NIAID Funds Cutting-Edge Genomics and Bioinformatics Programs
NIAID has announced six awards to continue the Genomics Centers for Infectious Diseases (GCIDs) and Bioinformatics Resource Centers (BRCs) for Infectious Diseases, both important data science networks offering critical resources for the scientific community.

Charting the Path to an HIV-Free Generation
NIAID supports four research networks as part of its HIV clinical research enterprise. Every seven years, the Institute engages research partners, community representatives, and other public health stakeholders in a multidisciplinary evaluation of network progress toward short- and long-term scientific goals. Pregnancy, childbirth and the postnatal period are a key focus of NIAID HIV research and call for measures to support the health of people who could become pregnant as well as their infants.
Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies Evaluated in Many HIV Cure Strategies
Many promising HIV cure strategies use broadly neutralizing antibodies, or bNAbs, which can neutralize a wide range of HIV variants, homing in on and binding to specific viral components, and then acting to destroy the virus by triggering an immune response. Several HIV bNAbs have been developed and tested to determine whether they can prevent or treat HIV. NIAID and partners are evaluating bNAb-based strategies alone and in combination with other immunity-enhancing strategies for HIV clearance in clinical trials in in Africa, North and South America, and Southeast Asia.


