3 Results
Topical Steroid Withdrawal Diagnostic Criteria Defined by NIH Researchers
March 14, 2025
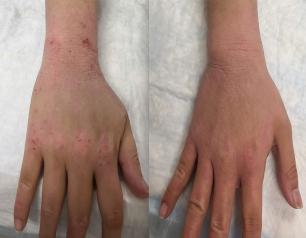
Topical steroid withdrawal (TSW) results in dermatitis that is distinct from eczema and is caused by an excess of NAD+, an essential chemical compound in the body, according to a new study from NIAID researchers.
NIAID Discovery Leads to Novel Probiotic for Eczema
June 26, 2024
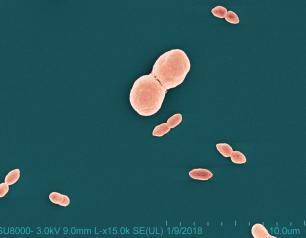
NIAID research has led to the availability of a new over-the-counter topical eczema probiotic. The probiotic is based on the discovery by scientists at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, that bacteria present on healthy skin called Roseomonas mucosa can safely relieve eczema symptoms in adults and children.
NIH Study of Early Predictors, Mechanisms of Food Allergy and Eczema has Begun
March 19, 2021
A study to identify prenatal and early childhood markers of high risk for food allergy and atopic dermatitis, or eczema, as well as biological pathways that lead to these conditions, has begun. The observational study of children from birth to age 3 years will examine the origins of allergic disease by integrating interdisciplinary analyses of data from more than 260 biological and environmental samples and survey responses from each of 2,500 families.


