59 Results
NIH-Sponsored Trial of Nasal COVID-19 Vaccine Opens
July 1, 2024
A Phase 1 trial testing the safety of an experimental nasal vaccine that may provide enhanced breadth of protection against emerging variants of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, is now enrolling healthy adults at three sites in the United States.
COVID-19 Vaccination and Boosting During Pregnancy Protects Infants for Six Months
February 14, 2024
Women who receive an mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccination or booster during pregnancy can provide their infants with strong protection against symptomatic COVID-19 infection for at least six months after birth. These findings reinforce the importance of receiving both a COVID-19 vaccine and booster during pregnancy to ensure that infants are born with robust protection that lasts until they are old enough to be vaccinated.

Clinical Trial to Test Immune Modulation Strategy for Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients Begins
September 22, 2023
A clinical trial has launched to test whether early intensive immune modulation for hospitalized COVID-19 patients with relatively mild illness is beneficial. The placebo-controlled study will enroll approximately 1,500 people at research sites around the world.
Severe COVID-19 May Lead to Long-Term Innate Immune System Changes
August 18, 2023
Severe COVID-19 may cause long-lasting alterations to the innate immune system, the first line of defense against pathogens, according to a small study funded by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
COVID-19 Vaccination and Boosting During Pregnancy Benefits Pregnant People and Newborns
August 11, 2023
Receiving a COVID-19 mRNA vaccine or booster during pregnancy can benefit pregnant people and their newborn infants, according to findings recently published in Vaccine. The paper describes results from the Multisite Observational Maternal and Infant Study for COVID-19 (MOMI-VAX), which was funded by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health.
The Potential and Challenges of Mucosal COVID-19 Vaccines
April 13, 2023
In November 2022, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) co-hosted a virtual workshop on the importance and challenges of developing mucosal vaccines for SARS-COV-2. The highlights of this workshop have now been published as a report in npj Vaccines.
SARS-CoV-2 Infection Weakens Immune-Cell Response to Vaccination
March 20, 2023
The magnitude and quality of a key immune cell’s response to vaccination with two doses of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine were considerably lower in people with prior SARS-CoV-2 infection compared to people without prior infection, a study has found. In addition, the level of this key immune cell that targets the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein was substantially lower in unvaccinated people with COVID-19 than in vaccinated people who had never been infected. Importantly, people who recover from SARS-CoV-2 infection and then get vaccinated are more protected than people who are unvaccinated.
NIH Trial to Evaluate Shionogi Antiviral in Adults Hospitalized with COVID-19
February 15, 2023
The National Institutes of Health has initiated a multi-site clinical trial evaluating an investigational antiviral for the treatment of COVID-19. The therapeutic, known as S-217622 or ensitrelvir fumaric acid, was discovered by Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan; and Shionogi & Co., Ltd., Osaka, Japan. The trial is assessing whether S-217622 can improve clinical outcomes for patients who are hospitalized for management of COVID-19 as compared to a placebo and will enroll approximately 1,500 people at sites worldwide.
Developing Mucosal Vaccines for Respiratory Viruses
January 11, 2023
Vaccines that provide long-lasting protection against influenza, coronaviruses and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) have proved exceptionally difficult to develop. In a new review article in Cell Host & Microbe, researchers from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the NIH, explore the challenges and outline approaches to improved vaccines. Anthony S. Fauci, M.D., former NIAID director, is an author along with Jeffery K. Taubenberger, M.D., Ph.D., and David M. Morens, M.D.
Findings Suggest COVID-19 Rebound Not Caused by Impaired Immune Response
October 6, 2022
Findings from a small study of eight patients published in Clinical Infectious Diseases suggest that COVID-19 rebound is likely not caused by impaired immune responses. The study, led by scientists at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, aimed to define the clinical course and the immunologic and virologic characteristics of COVID-19 rebound in patients who have taken nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (Paxlovid), an antiviral therapeutic developed by Pfizer, Inc.

SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Levels Linked to Patient Outcomes
August 29, 2022
The amount of SARS-CoV-2 antigen measured in the blood of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 is associated with illness severity and other clinical outcomes, according to a new study published in the Annals of Internal Medicine. The authors suggest that SARS-CoV-2 antigen levels hold promise as a biomarker, or a measurable substance, to predict which patients hospitalized with COVID-19 have a higher risk of worse outcomes.
Statement from NIH and BARDA on the Novavax COVID-19 Vaccine
July 20, 2022
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has recommended that Novavax’s COVID-19 vaccine be used as another primary series option for adults in the United States ages 18 years and older. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) previously authorized for emergency use the protein-based vaccine, known as NVX-CoV2373.
Vaccine-Induced Immune Response to Omicron Wanes Substantially Over Time
July 19, 2022
Although COVID-19 booster vaccinations in adults elicit high levels of neutralizing antibodies against the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2, antibody levels decrease substantially within 3 months, according to new clinical trial data. The findings, published today in Cell Reports Medicine, are from a study sponsored by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health. The trial was led by NIAID’s Infectious Diseases Clinical Research Consortium.
Food Allergy Is Associated with Lower Risk of SARS-CoV-2 Infection
June 1, 2022
A National Institutes of Health-funded study has found that people with food allergies are less likely to become infected with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, than people without them.
NIAID Announces Antiviral Drug Development Awards
May 18, 2022
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, has awarded approximately $577 million to establish nine Antiviral Drug Discovery (AViDD) Centers for Pathogens of Pandemic Concern.
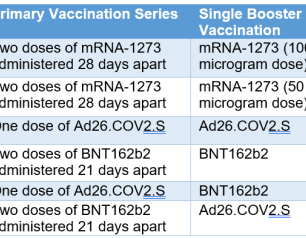
NIH Begins Clinical Trial Evaluating Second COVID-19 Booster Shots in Adults
March 31, 2022
A Phase 2 clinical trial evaluating various additional COVID-19 booster shots has begun enrolling adult participants in the United States. The trial aims to understand if different vaccine regimens—prototype and variant vaccines alone and in combinations—can broaden immune responses in adults who already have received a primary vaccination series and a first booster shot. The study, known as the COVID-19 Variant Immunologic Landscape (COVAIL) trial, is sponsored by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health.

NIH Experts Discuss Controlling COVID-19 in Commentary on Herd Immunity
March 31, 2022
Achieving classical herd immunity against SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, may not be attainable, according to a new perspective published in The Journal of Infectious Diseases. However, widespread use of currently available public health interventions to prevent and control COVID-19 will enable resumption of most activities of daily life with minimal disruption.
NIH Launches Trial to Study Allergic Reactions to COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine
March 9, 2022
Researchers from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) are conducting a clinical trial designed to help understand rare but potentially serious systemic allergic reactions to COVID-19 mRNA vaccines.
Leadership Transition at the NIAID Vaccine Research Center
February 16, 2022
Dr. Fauci expresses gratitude to John R. Mascola, M.D., as he announces his retirement as Director of the Dale and Betty Bumpers Vaccine Research Center at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
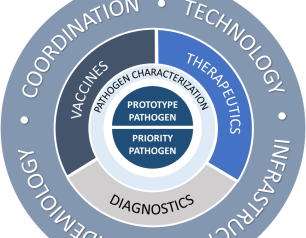
NIAID Pandemic Preparedness Plan Targets ‘Prototype’ and Priority Pathogens
February 2, 2022
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases is focusing on preparing for a range of other viral threats that could cause a public health emergency, and according to NIAID’s new Pandemic Preparedness Plan, the institute will direct its preparedness efforts on two fronts.
Trial Tests Strategy to Augment Response to COVID-19 Vaccines in Transplant Recipients
January 31, 2022
A study has begun to assess the antibody response to an additional dose of a COVID-19 mRNA vaccine in kidney and liver transplant recipients, either alone or with a concurrent reduction in immunosuppressive medication.
Hyperimmune Intravenous Immunoglobulin Does Not Improve Outcomes for Adults Hospitalized with COVID-19
January 27, 2022
A clinical trial has found that the combination of remdesivir plus a highly concentrated solution of antibodies that neutralize SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, is not more effective than remdesivir alone for treating adults hospitalized with the disease.
Mix-and-Match Trial Finds Additional Dose of COVID-19 Vaccine Safe, Immunogenic
January 26, 2022
In adults who had previously received a full regimen of any of three COVID-19 vaccines granted Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) or approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), an additional booster dose of any of these vaccines was safe and prompted an immune response, according to preliminary clinical trial results reported in The New England Journal of Medicine. The findings served as the basis for recommendations by the FDA and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in late fall 2021 to permit mix-and-match COVID-19 booster vaccinations in the United States.
Lung Autopsies of COVID-19 Patients Reveal Treatment Clues
November 17, 2021
Lung autopsy and plasma samples from people who died of COVID-19 have provided a clearer picture of how the SARS-CoV-2 virus spreads and damages lung tissue.
Long-Term Study of Children with COVID-19 Begins
November 15, 2021
A large, long-term study of the impacts of COVID-19 on children has enrolled its first participant at the National Institutes of Health’s Clinical Center in Bethesda, Maryland. The study, which is supported by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, will track up to 1,000 children and young adults who previously tested positive for COVID-19 and evaluate the impact of COVID-19 on their physical and mental health over three years.


