10 Results
Tecovirimat Is Safe but Ineffective as Treatment for Clade II Mpox
March 12, 2025
Monotherapy with the antiviral drug tecovirimat was safe but ineffective as an mpox treatment in an international clinical trial.
NIH Officials Assess Threat of H5N1
December 31, 2024
HPAI H5N1 influenza remains a low risk to most Americans, but that does not diminish concern about the virus, NIAID experts say.
NIH Study Finds Tecovirimat Was Safe but Did Not Improve Mpox Resolution or Pain
December 10, 2024
Tecovirimat was safe but did not reduce the time to lesion resolution or reduce pain among adults with mild to moderate clade II mpox and a low risk of severe disease in an international study.
Bovine H5N1 Influenza from Infected Worker Transmissible and Lethal in Animal Models
October 28, 2024
Bovine H5N1 influenza virus taken from eye of infected worker transmissible and lethal in animal models.
NIH Releases Mpox Research Agenda
September 17, 2024
The NIAID mpox research agenda focuses on four key objectives: increasing knowledge about the biology of all clades—also known as strains—of the virus that causes mpox, including how the virus is transmitted and how people’s immune systems respond to it; evaluating dosing regimens of current vaccines to stretch the vaccine supply and developing novel vaccine concepts; advancing existing and novel treatments, including antivirals and monoclonal antibodies; and supporting strategies for detecting the virus to facilitate clinical care and epidemiological surveillance.

NIH Releases Strategic Plan for Research on Herpes Simplex Virus 1 and 2
September 19, 2023
In response to the persistent health challenges of herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) and HSV-2, an NIH-wide HSV Working Group developed the plan, informed by feedback from more than 100 representatives of the research and advocacy communities and interested public stakeholders. The plan outlines an HSV research framework with four strategic priorities: improving fundamental knowledge of HSV biology, pathogenesis, and epidemiology; accelerating research to improve HSV diagnosis; improving strategies to treat HSV while seeking a curative therapeutic; and, advancing research to prevent HSV infection.

NIH Awards $12 Million for Antiviral Therapeutic Development
November 21, 2022
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, recently awarded more than $12 million to three institutions for the development of antiviral therapies to treat diseases caused by viruses with pandemic potential. NIAID may award approximately $61.5 million total over five years if all contract options are exercised.
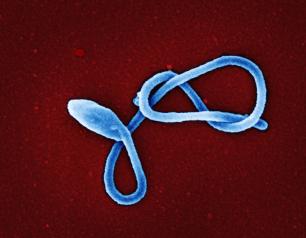
U.S. Clinical Trial Evaluating Antiviral for Monkeypox Begins
September 9, 2022
A Phase 3 clinical trial evaluating the antiviral tecovirimat, also known as TPOXX, is now enrolling adults and children with monkeypox infection in the United States. Study investigators aim to enroll more than 500 people from clinical research sites nationwide. Interested volunteers can visit the ACTG website (clinical trial A5418) for more information. The NIAID-funded Advancing Clinical Therapeutics Globally for HIV/AIDS and Other Infections (ACTG) is leading the study, which may later expand to international sites. The Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD) at NIH is supporting several sites, including through the International Maternal Pediatric Adolescent AIDS Clinical Trials Network (IMPAACT).
NIAID Announces Antiviral Drug Development Awards
May 18, 2022
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, has awarded approximately $577 million to establish nine Antiviral Drug Discovery (AViDD) Centers for Pathogens of Pandemic Concern.
Biden Administration to Invest $3 Billion from American Rescue Plan as Part of COVID-19 Antiviral Development Strategy
June 17, 2021
Through collaboration within the HHS, including NIH, NIAID, and BARDA, the Antiviral Program for Pandemics will respond to the urgent need for antivirals to treat COVID-19.

