Autoimmunity and Functional Genomics Section
Silvia Bolland, Ph.D.
Chief, Autoimmunity and Functional Genomics Section

Major Areas of Research
- Identification of new genetic modifiers of systemic autoimmune disease
- Dose effect of Toll-like receptor genes and its role in autoimmune pathologies
- Inhibitory signaling pathways mediated by the IgG Fc receptor (Fc gamma RIIB) and the phosphoinositol 5-phosphatase (SHIP)
Program Description
Our group is interested in immune inhibitory pathways and their role in preventing autoimmunity.
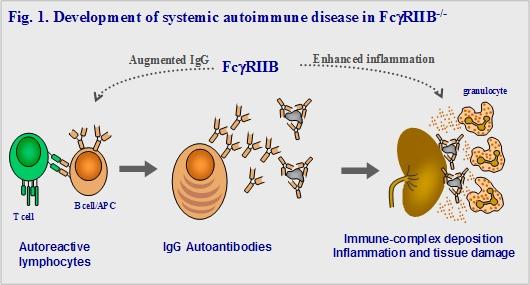
Fig. 1. We have generated a new model for systemic autoimmune disease in mice deficient in FcγRIIB, an IgG-binding receptor that inhibits antibody production and inflammatory responses.These mice develop a spontaneous disease that resembles lupus in humans, but only in certain genetic backgrounds. We are studying genetic modifiers that augment susceptibility and severity of disease so that we can understand cellular mechanisms that induce these pathologies and identify new genes that can be used as therapeutic targets.
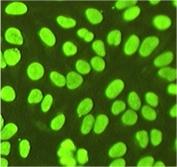
Figure 2a. Addition of the Y chromosome-linked Yaa modifier in the FcγRII-ko lupus model results in aggravated glomerulonephritis and a switch from anti-chromatin to anti-nucleolar autoantibodies.
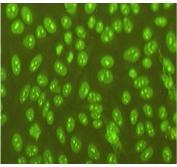
Figure 2b. Addition of the Y chromosome-linked Yaa modifier in the FcγRII-ko lupus model results in aggravated glomerulonephritis and a switch from anti-chromatin to anti-nucleolar autoantibodies.
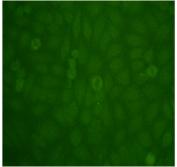
Figure 2c. Addition of the Y chromosome-linked Yaa modifier in the FcγRII-ko lupus model results in aggravated glomerulonephritis and a switch from anti-chromatin to anti-nucleolar autoantibodies.
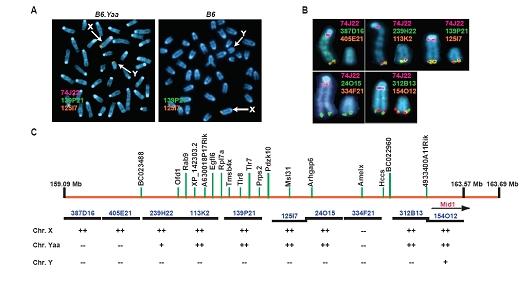
Figure 3. We have shown that the nucleolar specificity of Yaa-derived antibodies is a B-cell-intrinsic feature resulting from a large genomic duplication that includes the TLR7 gene. Our future experiments will explore expression levels of Toll-like receptors and other genetic factors that regulate the development of autoimmunity.
Biography
Education
Ph.D., University of Cantabria, Spain
Dr. Bolland received her Ph.D. in molecular biology from the University of Cantabria, Spain, and received postdoctoral training at Harvard and The Rockefeller University. She joined the NIAID Laboratory of Immunogenetics in September 2001. She is the recipient of an S.L.E. Foundation Career Development Award and a Novel Research Grant Award from the Lupus Research Institute.
Selected Publications
Leung WH, Tarasenko T, Biesova Z, Kole H, Walsh ER, Bolland S. Aberrant antibody affinity selection in SHIP-deficient B cells.Eur J Immunol. 2013 Feb;43(2):371-81.
Walsh ER, Pisitkun P, Voynova E, Deane JA, Scott BL, Caspi RR, Bolland S. Dual signaling by innate and adaptive immune receptors is required for TLR7-induced B-cell-mediated autoimmunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Oct 2;109(40):16276-81.
Crampton SP, Deane JA, Feigenbaum L, Bolland S. Ifih1 gene dose effect reveals MDA5-mediated chronic type I IFN gene signature, viral resistance, and accelerated autoimmunity. J Immunol. 2012 Feb 1;188(3):1451-9.
Waisberg M, Tarasenko T, Vickers BK, Scott BL, Willcocks LC, Molina-Cruz A, Pierce MA, Huang CY, Torres-Velez FJ, Smith KG, Barillas-Mury C, Miller LH, Pierce SK, Bolland S. Genetic susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus protects against cerebral malaria in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jan 18;108(3):1122-7.
Crampton SP, Voynova E, Bolland S. Innate pathways to B-cell activation and tolerance. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010 Jan;1183:58-68.
Bolland S. An innate path to human B cell tolerance. Immunity. 2008 Nov 14;29(5):667-9.
Research Group

Left to right: Top: Juan Wu, Silvia Bolland, Hemanta Kole, Hongsheng Wang. Bottom: Laura Amo, Bethany Scott.

