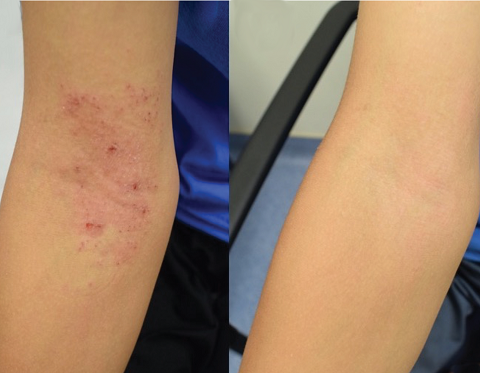
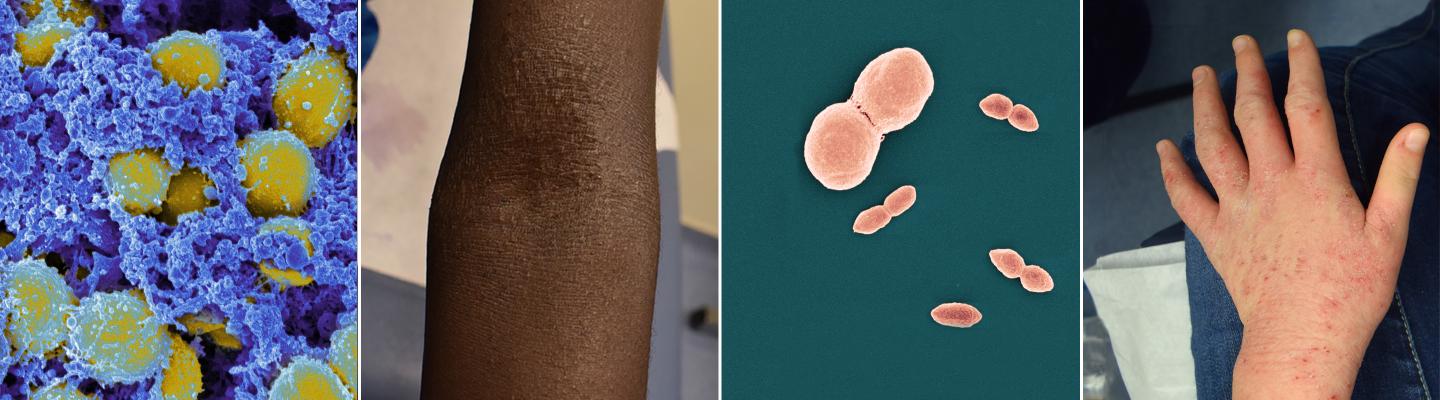
Recommended Treatments for Eczema
The two largest American professional associations of allergists and immunologists jointly recommend several types of products for the treatment of eczema, including topical and systemic medications. The recommendations vary in strength based on the quality of available evidence and differ by severity of disease. For a summary of the 2024 guidelines, please visit the Updated Guidelines for Atopic Dermatitis—AAAAI/ACAAI Joint Task Force.
NIAID’s Eczema Treatment Research
NIAID-supported research on eczema therapeutics currently focuses on topical probiotics—medications that use bacteria found on healthy skin to attempt to treat the disease. The bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms that live on the skin, collectively called the skin microbiome, normally support the skin in preventing infection and water loss among other healthy functions. People with eczema experience imbalances in the skin microbiome. Scientists are studying whether probiotics can restore a healthy balance of skin microorganisms in people with eczema and thus alleviate their symptoms.
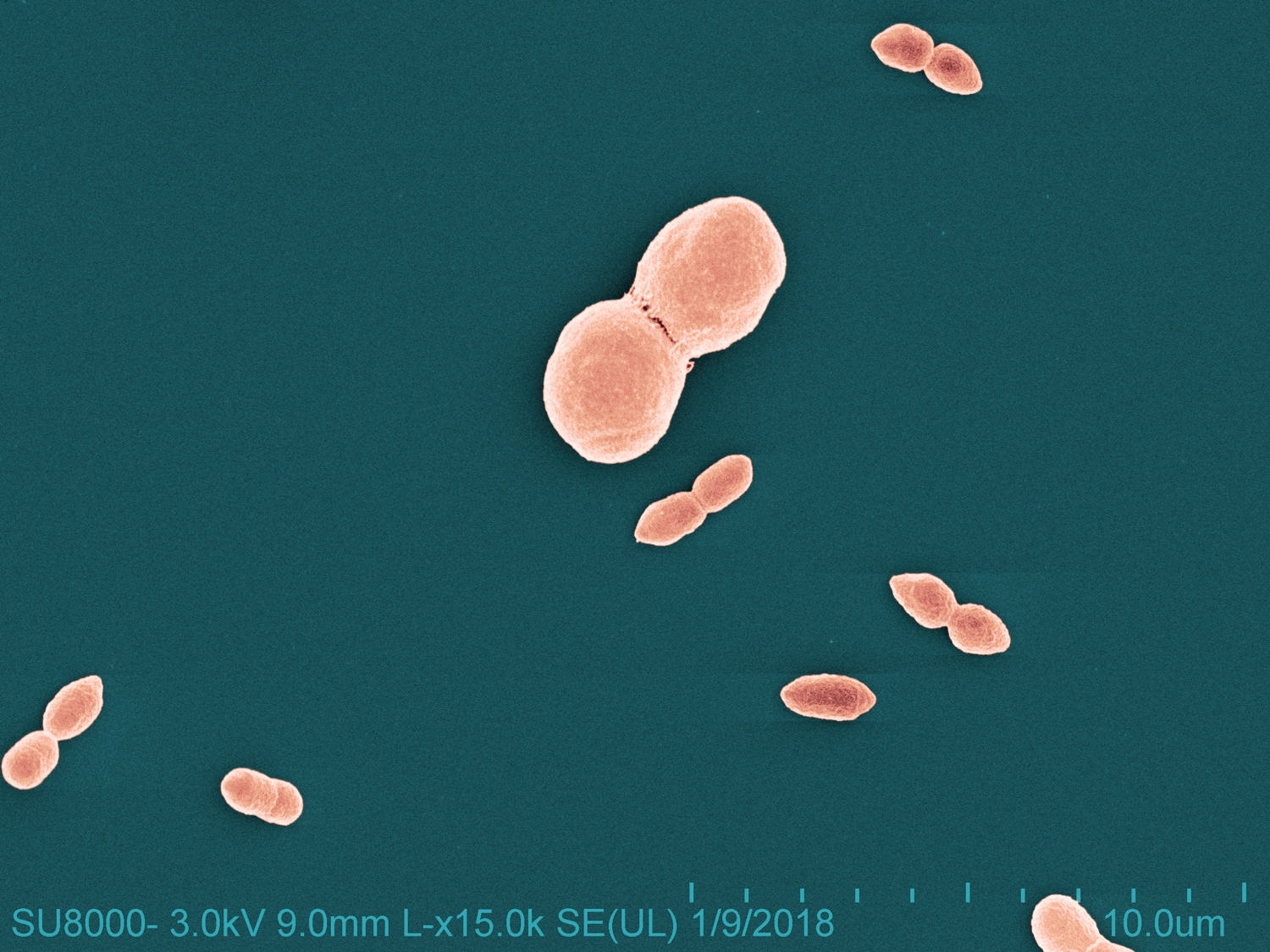
Research in NIAID’s Laboratory of Clinical Microbiology and Immunology led to the availability in June 2024 of a novel over-the-counter probiotic based on a strain of the bacteria Roseomonas mucosa, which occurs naturally as part of a typical skin microbiome. The researchers isolated and cultured R. mucosa and demonstrated in laboratory, animal, and human studies that it can help restore skin lipids (oils) deficient in people with eczema.
To potentially expand the use of R. mucosa, NIAID launched a clinical trial in 2024 to generate further evidence on its efficacy in reducing eczema symptoms. More information about this trial and contact information for people interested in participating are available in ClinicalTrials.gov under study identifier NCT06096857.
In addition, the NIAID-funded Atopic Dermatitis Research Network is preparing to launch a clinical trial in 2025 to assess the safety and efficacy of bacteria found on healthy human skin as a topical therapy for eczema. The bacteria, Staphylococcus hominis A9, showed promise for treating eczema in animal studies. A preliminary clinical trial of S. hominis A9 in people with the disease suggested the treatment was safe. The new clinical trial will take place in multiple cities across the United States. Detailed information about the trial, including the locations and contact information for people interested in participating, is available at ClinicalTrials.gov under study identifier NCT06504160.
Scientific Advances
Topical Steroid Withdrawal Diagnostic Criteria Defined by NIH Researchers
March 14, 2025Topical steroid withdrawal (TSW) results in dermatitis that is distinct from eczema and is caused by an excess of NAD+, an essential chemical compound in the body, according to a new study from NIAID researchers.

NIAID Discovery Leads to Novel Probiotic for Eczema
June 26, 2024NIAID research has led to the availability of a new over-the-counter topical eczema probiotic. The probiotic is based on the discovery by scientists at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, that bacteria present on healthy skin called Roseomonas mucosa can safely relieve eczema symptoms in adults and children.
Probiotic Skin Therapy Improves Eczema in Children, NIH Study Suggests
September 9, 2020An experimental treatment for eczema safely reduced disease severity and increased quality of life for children as young as 3 years old, NIH study shows.