39 Results
World Neglected Tropical Diseases Day – Focus on Leishmaniasis
World Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTD) Day offers an opportunity to reflect on recent strides in tropical disease research and the work that remains. NIAID conducts and supports work on a wide variety of diseases—some of which rarely make headlines but cause immense suffering. An example of this is leishmaniasis, a parasitic disease that sickens hundreds of thousands of people each year, mostly in equatorial regions of the globe. In recent years, NIAID has made significant efforts to study the parasite that causes the disease and find new ways to battle it.
Scientists Identify Interferon-gamma as Potential SARS-CoV-2 Antiviral
Conditioning the lungs with interferon-gamma, a natural immune system protein best known for fighting bacterial infections, appears to be a strong antiviral for SARS-CoV-2, which causes COVID-19
NIAID Team Explores Metabolism in Determining Infection Severity
The route a pathogen takes in causing infection can determine the severity of disease. NIAID scientists are looking at metabolism to determine how and why there is a difference.

Building a Better Malaria Vaccine—NIAID Researchers Design a Paradigm-Busting Candidate
NIAID researchers used structural information about two malaria parasite proteins along with mechanistic information about the interaction between them to design and build an entirely novel candidate vaccine. When tested in rats, their “structure-based design 1” (SBD1) immunogen vaccine performed better than other experimental malaria vaccines. It also upends the conventional wisdom that successful vaccines must elicit receptor-blocking antibodies.
NIAID Researchers Study Causes of Brain Swelling in Cerebral Malaria
In children with cerebral malaria, brain swelling can cause seizures, coma, and death. Researchers from NIAID and their colleagues studied children with cerebral malaria in Malawi to better understand the underlying causes of these devastating symptoms.

Promising Experimental Vaccine for Tick-borne Kyasanur Forest Disease Virus
With ticks expanding their territories in many parts of the world, a NIAID research group has likewise expanded its promising vaccine research to two typically rare pathogens with potential for public health importance -- Kyasanur Forest disease and Alkhurma hemorrhagic fever.
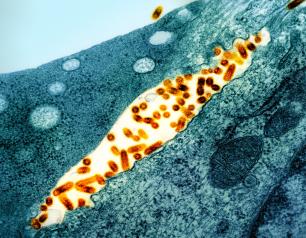
Ohio State Scientists Evaluate Role of Deer in SARS-CoV-2 Transmission
SARS-CoV-2 evolves three times faster in white-tailed deer than in people, making NIAID-funded scientists at The Ohio State University and colleagues ask whether deer are an important reservoir for emerging virus variants.
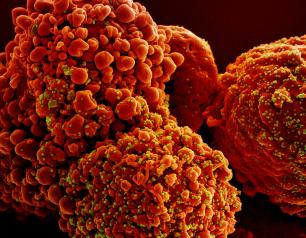
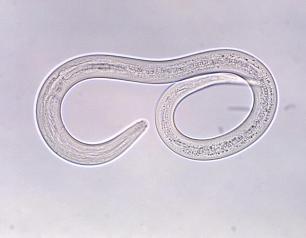
Relation of Parasitic Worm Infection and SARS-CoV-2 Explored
NIAID researchers used mice to investigate a possible relationship between parasitic worm infection and resistance to severe COVID-19.
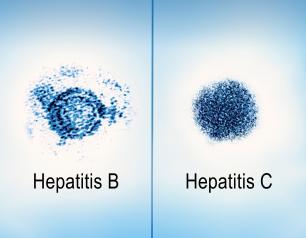
Hepatitis B and C—A Closer Look at NIAID Research to Accelerate Elimination
Viral hepatitis is an inflammatory liver disease caused by infection with any of the known hepatitis viruses—A, B, C, D, and E. Most of the global viral hepatitis burden is from hepatitis B and C, which affect 354 million people and result in 1.1 million deaths annually. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that in 2020 there were 14,000 and 50,300 new acute infections of...
Close-up view of protein-complex structures could lead to better flu vaccines
A new understanding of vaccine components gained through electron microscopy and other direct visualization techniques could help scientists design more effective seasonal influenza vaccines.
Some Reported Allergic Reactions to mRNA COVID-19 Vaccines Were Likely Stress Responses
Some responses to the mRNA COVID-19 vaccines reported as severe allergic reactions were likely a recently described, non-allergic condition called immunization stress-related response (ISRR), according to a study by investigators. The symptoms of ISRR can closely mimic those of a severe allergic reaction known as anaphylaxis, a potentially life-threatening, systemic allergic reaction in which the immune system releases a dangerous flood of chemicals.

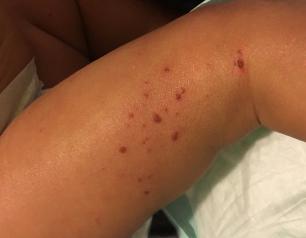
NIAID Researchers Identify Link Between Common Chemicals and Eczema
NIAID scientists have found an association between widely used chemicals called diisocyanates and atopic dermatitis, a chronic inflammatory skin disease commonly known as eczema.
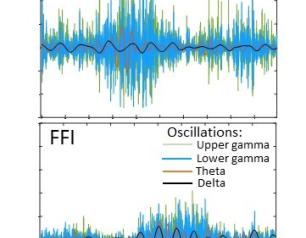
Novel Study Model Reveals New Understanding of Fatal Familial Insomnia
Fatal familial insomnia (FFI) is a little-known yet horrific disease in which people die from lack of sleep. In a new study, NIAID scientists developed a cerebral organoid model to study the exact protein mutation that causes FFI.
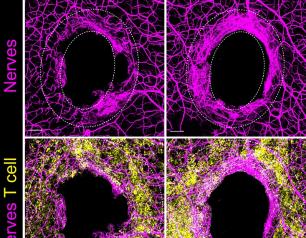
NIAID-led Work Identifies Bacteria Signaling for Nerve Repair in Mice
A team of NIAID-led researchers has identified a mechanism in mice in which the immune system and commensal bacteria help repair damaged sensory neurons within the skin. They hope their findings could lead to therapies that stimulate recovery in people following skin injury and limit damage from chemotherapy and chronic diseases.