40 Results
Measuring Innovation: Laboratory Infrastructure to Deliver Essential HIV Clinical Trial Results
HIV clinical trials network laboratory functions will continue to evolve to align with scientific priorities and research approaches.
Some People with Advanced HIV Have Anti-CD4 Autoantibodies Associated with Dampened Immune Recovery
A NIAID-sponsored analysis found that people with advanced HIV and anti-CD4 autoantibodies experienced limited CD4+ T-cell reconstitution through up to four years of observation after ART initiation, highlighting a potential immune effect of long-term unsuppressed HIV. The findings were published in Clinical Infectious Diseases.
Scientists Discover Cause, Potential Treatment for Cases of Deadly Autoimmune Disorder
Discovery of a gene variant causing some cases of APECED, a rare inherited autoimmune disease, will enable earlier diagnosis & medical care that may prolong lives.
Shaping the Next Era of HIV Therapeutics and Care
The Institute aims to foster the next generation of discoveries that will enable people with HIV to experience a typical lifespan with high life quality. Scientific priorities include removing the chronic HIV medication burden; reducing the incidence of concurrent TB and hepatitis; and ensuring scientific advances can feasibly be scaled to all who stand to benefit.
HIVR4P 2024 Research Highlights: Reproductive Health While on PrEP and Signals to Guide HIV Vaccines and Cure
New NIAID-supported science presented at the 2024 HIV Research for Prevention conference in Lima, Peru features a breadth of HIV discovery and translational findings and enriches the evidence base on HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis within the context of reproductive health.
Defining the Goals of HIV Science Through 2034
Discovery, Development and Delivery for an Increasingly Interconnected HIV Landscape
By Carl Dieffenbach, Ph.D., director, Division of AIDS, NIAID
We envision an HIV research enterprise that follows a logical evolution in addressing new scientific priorities informed by previous research progress. We will fund our next networks to align with updated research goals to take us through the end of 2034. Our capacity must reflect an increasing interdependence across clinical practice areas and public health contexts.
Fungal Disease Awareness Week—Fighting Fungi at NIAID
Fungal Disease Awareness Week spotlights clinical trials of improved treatments for fungal infections, such as better use of antibiotics and treatment combinations.
Study Links Certain Vaginal Bacteria and Inflammatory Marker to Increased Odds of Acquiring HIV Among Cisgender Women
Fourteen vaginal bacterial species and the presence of a protein that promotes inflammation were associated with increased odds of HIV acquisition in a study of more than 500 cisgender women in African countries with high HIV incidence. The study was the largest to date to prospectively analyze the relationship between both the vaginal microbiome and vaginal tissue inflammation and the likelihood of acquiring HIV among cisgender women in this population.
Bringing HIV Study Protocols to Life with Representative, High-Quality Research
The HIV clinical trials network sites have made tremendous contributions to NIH’s scientific priorities by offering direct access to and consultation with populations most affected by HIV globally, and by delivering high-quality clinical research with strong connections to trusted community outreach platforms. Future networks will need to maintain core strengths of current models while expanding capacity in areas vital to further scientific progress. These include operations that inform pandemic responses and extending our reach within communities impacted by HIV, including populations historically underrepresented in clinical research.
Charting the Path to an HIV-Free Generation
NIAID supports four research networks as part of its HIV clinical research enterprise. Every seven years, the Institute engages research partners, community representatives, and other public health stakeholders in a multidisciplinary evaluation of network progress toward short- and long-term scientific goals. Pregnancy, childbirth and the postnatal period are a key focus of NIAID HIV research and call for measures to support the health of people who could become pregnant as well as their infants.
Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies Evaluated in Many HIV Cure Strategies
Many promising HIV cure strategies use broadly neutralizing antibodies, or bNAbs, which can neutralize a wide range of HIV variants, homing in on and binding to specific viral components, and then acting to destroy the virus by triggering an immune response. Several HIV bNAbs have been developed and tested to determine whether they can prevent or treat HIV. NIAID and partners are evaluating bNAb-based strategies alone and in combination with other immunity-enhancing strategies for HIV clearance in clinical trials in in Africa, North and South America, and Southeast Asia.

AIDS 2024: Long-Acting Injectables, Bi-Directional Learning, PACHA & More (VIDEO)
HIV.gov continued daily coverage of AIDS 2024. Tune in to four conversations livestreamed at the conference.
A New Way to Measure and Predict Human Immune Health
The immune system senses and responds to changes in physiologic health, and a new tool called the immune health metric (IHM) can measure and even predict some of these changes, an NIAID study has found. If doctors could use the IHM to detect health problems long before symptoms appear, they could potentially act early to prevent disease, the investigators suggest.
The Hidden Link Between Malaria and Lupus
Scientists have long been aware that malaria infection is associated with high levels of autoantibodies—antibodies that recognize and attack the person’s own tissues and are associated with autoimmune disorders. NIAID researchers, along with their colleagues, have studied the molecular mechanisms of these autoantibodies. Their findings reveal the associations between malaria, human resistance to it, and autoantibodies that are linked to certain autoimmune disorders—specifically, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Antiretroviral Drug Improves Kidney Function After Transplant in People with HIV
An HIV drug that suppresses the activity of the CCR5 receptor—a collection of proteins on the surface of certain immune cells—was associated with better renal function in kidney transplant recipients with HIV compared to people who took a placebo in a randomized trial. According to the authors, these findings warrant further exploration of the benefit of CCR5 antagonists in all kidney transplant recipients regardless of HIV status. The findings of the NIAID-sponsored trial were presented today at the 2024 American Transplant Congress in Philadelphia.
Unpacking the Interplay between Autoimmunity and Immunodeficiency
The presence of antibodies that target one of the body’s own proteins was associated with severe infections that typically only occur when a person’s immune system is suppressed, based on a multi-cohort study of blood samples from more than 1,000 people. This study suggests autoimmune processes could be involved in the development of immunodeficiency in adulthood.
NIAID Research Team Develops 2nd Model of Crimean-Congo Fever
A NIAID research team has developed an additional nonhuman primate study model for Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever (CCHF), providing an alternative for development of critically needed vaccines and therapeutics.
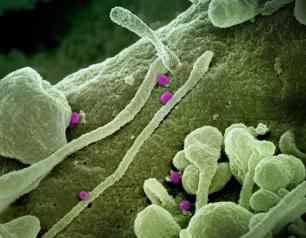
Proof-of-Concept Study Shows an HIV Vaccine Can Generate Key Antibody Response in People
An HIV vaccine candidate elicited trace levels of HIV broadly neutralizing antibodies and high levels of other key immune cells in an early-stage clinical trial. This immune response is an important signal that, if antibody levels can be further amplified, the vaccination strategy might be able to prevent HIV.
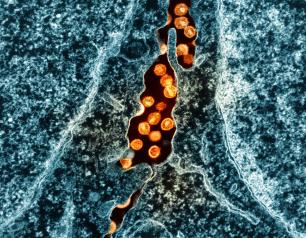
NIAID Marks HIV Vaccine Awareness Day 2024
On the 27th observance of HIV Vaccine Awareness Day (Saturday, May 18), we express our gratitude to the dedicated global community of scientists, advocates, study participants, study staff, and funders working toward a safe, effective, durable, and accessible HIV vaccine.
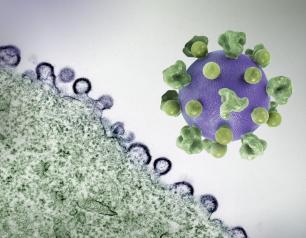
Exploring a Meningitis Vaccine for Gonorrhea Prevention
A preventive vaccine for gonorrhea would be a major advance in public health, according to an editorial co-authored by NIAID Director Jeanne Marrazzo. The genetic sequences of the bacteria that cause gonorrhea and meningitis B, are closely related. This has led researchers to explore whether the 4CMenB vaccine, approved by the Food and Drug Administration for meningitis B, might also prevent gonorrhea. NIAID is sponsoring an efficacy study of the 4CMenB vaccine for gonorrhea prevention.
Championing Asthma Research to Reduce the Burden of Disease
Today on World Asthma Day, NIAID reaffirms its commitment to reducing illness from this chronic lung syndrome and improving quality of life for people with asthma through research that informs the development of new asthma prevention and treatment strategies. NIAID-funded studies recently uncovered new risk factors for asthma and a previously unreported cause of frequent, severe asthma attacks. Other studies shed light on poorly understood causes of airway inflammation, as well as on genes and proteins involved in regulating asthma severity.
The HIV Field Needs Early-Stage Investigators (VIDEO)
by Jeanne Marrazzo, M.D., M.P.H., NIAID Director
The HIV research community is led by scientists with deep personal commitments to improving the lives of people with and affected by HIV. Our collective decades of work have generated HIV testing, prevention and treatment options beyond what we could have imagined in the 1980s. Those advances enable NIAID to explore new frontiers: expanding HIV prevention and treatment modalities, increasing understanding of the interplay between HIV and other infectious and non-communicable diseases, optimizing choice and convenience, and building on the ever-growing knowledge base that we need to develop a preventive vaccine and cure. The next generation of leaders will bring these concepts to fruition, and we need to welcome and support them into the complex and competitive field of HIV science.
Sexually Transmitted Infections—A Closer Look at NIAID Research
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites. NIAID supports research across the spectrum from basic to clinical science to develop effective diagnostic, preventive and therapeutic approaches to STIs in alignment with the National STI Strategic Plan. In recognition of National STI Awareness Week, NIAID shares a snapshot of new projects and recent scientific advances in STI research.
NIH Ending the HIV Epidemic Projects Bridge Gaps Between HIV Research and Public Health Practice (VIDEO)
The National Institutes of Health recently issued $26M in awards to HIV research institutions in its fifth year supporting implementation science under the Ending the HIV Epidemic in the U.S. initiative. These awards are the latest investments in a program that is rapidly and rigorously generating evidence to inform the unified domestic HIV response by agencies in the Department of Health and Human Services.
Stem Cell Changes Rejuvenate Immune System in Aged Mice
Using a mouse model of human aging and disease, NIAID scientists and Stanford University colleagues have shown that immune systems of aged laboratory mice can be made more youthful and effective at fighting disease by depleting a subset of haematopoietic stem cells.