48 Results
Trial of Potential Universal Flu Vaccine Opens at NIH Clinical Center
June 28, 2022
A Phase 1 clinical trial of a novel influenza vaccine has begun inoculating healthy adult volunteers at the National Institutes of Health Clinical Center in Bethesda, Maryland. The placebo-controlled trial will test the safety of a candidate vaccine, BPL-1357, and its ability to prompt immune responses.
NIAID Director Fauci Tests Positive for COVID-19
June 15, 2022
Anthony S. Fauci, M.D., director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), tested positive for COVID-19 on a rapid antigen test.
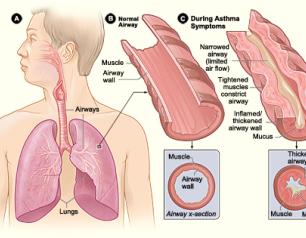
NIH Launches Trial of Monoclonal Antibody to Treat Asthma in Urban Youth
June 2, 2022
The National Institutes of Health has launched a clinical trial testing whether a monoclonal antibody, dupilumab, can reduce asthma attacks and improve lung function and asthma symptoms in children with poorly controlled allergic asthma who live in low-income urban neighborhoods.
Food Allergy Is Associated with Lower Risk of SARS-CoV-2 Infection
June 1, 2022
A National Institutes of Health-funded study has found that people with food allergies are less likely to become infected with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, than people without them.
Combination Anti-HIV Antibody Infusions Suppress Virus for Prolonged Period
June 1, 2022
According to a small study published today in the journal Nature, individuals with HIV who began taking antiretroviral therapy (ART) in the early stages of infection achieved a lengthy period of HIV suppression without ART after receiving two broadly neutralizing anti-HIV antibodies (bNAbs).
NIAID Announces Antiviral Drug Development Awards
May 18, 2022
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, has awarded approximately $577 million to establish nine Antiviral Drug Discovery (AViDD) Centers for Pathogens of Pandemic Concern.
Vaccine for Rare but Deadly Mosquito-Borne Viruses Shows Promise in Clinical Trial
May 12, 2022
A vaccine for eastern equine encephalitis virus (EEEV), western equine encephalitis virus (WEEV), and Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus (VEEV) was found to be safe, well-tolerated and induced a neutralizing antibody response in adult volunteers, according to newly published results from a Phase 1 clinical trial.

NIH Launches Clinical Trial of Epstein-Barr Virus Vaccine
May 6, 2022
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, has launched an early-stage clinical trial to evaluate an investigational preventative vaccine for Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). EBV is the primary cause of infectious mononucleosis and is associated with certain cancers and autoimmune diseases. The Phase 1 study, which will be conducted at the NIH Clinical Center in Bethesda, Maryland, is one of only two studies to test an investigational EBV vaccine in more than a decade.
NIAID Marks World Malaria Day
April 25, 2022
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), reaffirms our commitment to developing safe and effective medical tools against malaria, and, in the words of this year’s World Malaria Day theme, “Harnessing innovation to reducing the malaria disease burden and saving lives.”
NIH Funds New Tuberculosis Research Advancement Centers
April 6, 2022
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, today announced four new grant awards to establish Tuberculosis Research Advancement Centers (TRACs)
NIH Begins Clinical Trial Evaluating Second COVID-19 Booster Shots in Adults
March 31, 2022
A Phase 2 clinical trial evaluating various additional COVID-19 booster shots has begun enrolling adult participants in the United States. The trial aims to understand if different vaccine regimens—prototype and variant vaccines alone and in combinations—can broaden immune responses in adults who already have received a primary vaccination series and a first booster shot. The study, known as the COVID-19 Variant Immunologic Landscape (COVAIL) trial, is sponsored by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health.

NIH Experts Discuss Controlling COVID-19 in Commentary on Herd Immunity
March 31, 2022
Achieving classical herd immunity against SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, may not be attainable, according to a new perspective published in The Journal of Infectious Diseases. However, widespread use of currently available public health interventions to prevent and control COVID-19 will enable resumption of most activities of daily life with minimal disruption.
World TB Day 2022—Invest to End TB. Save Lives
March 24, 2022
Today marks the 140th anniversary of the announcement by Dr. Robert Koch that tuberculosis (TB) is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. World TB Day is a reminder that this ancient disease remains a relentless killer. The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, affirms its commitment to the 2022 World TB Day theme, Invest to End TB. Save Lives, by supporting and conducting wide-ranging research aimed at reducing the health and economic impacts of TB.
NIH Launches Clinical Trial of Three mRNA HIV Vaccines
March 14, 2022
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, has launched a Phase 1 clinical trial evaluating three experimental HIV vaccines based on a messenger RNA (mRNA) platform—a technology used in several approved COVID-19 vaccines. NIAID is sponsoring the study, called HVTN 302, and the NIAID-funded HIV Vaccine Trials Network (HVTN), based at Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, is conducting the trial.
NIH Launches Trial to Study Allergic Reactions to COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine
March 9, 2022
Researchers from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) are conducting a clinical trial designed to help understand rare but potentially serious systemic allergic reactions to COVID-19 mRNA vaccines.
Leadership Transition at the NIAID Vaccine Research Center
February 16, 2022
Dr. Fauci expresses gratitude to John R. Mascola, M.D., as he announces his retirement as Director of the Dale and Betty Bumpers Vaccine Research Center at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
Researchers Document Third Known Case of HIV Remission Involving Stem Cell Transplant
February 15, 2022
A woman with HIV who received a cord blood stem cell transplant to treat acute myeloid leukemia has had no detectable levels of HIV for 14 months despite cessation of antiretroviral therapy (ART), according to a presentation at today’s Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI).
NIAID Pandemic Preparedness Plan Targets ‘Prototype’ and Priority Pathogens
February 2, 2022
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases is focusing on preparing for a range of other viral threats that could cause a public health emergency, and according to NIAID’s new Pandemic Preparedness Plan, the institute will direct its preparedness efforts on two fronts.
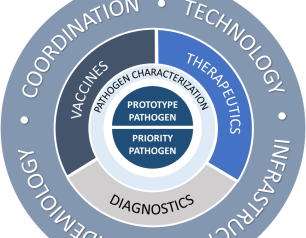
NIH Supports Valley Fever Research with New Awards
February 2, 2022
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases has announced three awards to establish a network of Coccidioidomycosis Collaborative Research Centers to conduct research on coccidioidomycosis, also known as Valley Fever.
Trial Tests Strategy to Augment Response to COVID-19 Vaccines in Transplant Recipients
January 31, 2022
A study has begun to assess the antibody response to an additional dose of a COVID-19 mRNA vaccine in kidney and liver transplant recipients, either alone or with a concurrent reduction in immunosuppressive medication.
Hyperimmune Intravenous Immunoglobulin Does Not Improve Outcomes for Adults Hospitalized with COVID-19
January 27, 2022
A clinical trial has found that the combination of remdesivir plus a highly concentrated solution of antibodies that neutralize SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, is not more effective than remdesivir alone for treating adults hospitalized with the disease.
Mix-and-Match Trial Finds Additional Dose of COVID-19 Vaccine Safe, Immunogenic
January 26, 2022
In adults who had previously received a full regimen of any of three COVID-19 vaccines granted Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) or approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), an additional booster dose of any of these vaccines was safe and prompted an immune response, according to preliminary clinical trial results reported in The New England Journal of Medicine. The findings served as the basis for recommendations by the FDA and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in late fall 2021 to permit mix-and-match COVID-19 booster vaccinations in the United States.
Oral Immunotherapy Induces Remission of Peanut Allergy in Some Young Children
January 20, 2022
A clinical trial funded by the National Institutes of Health has found that giving peanut oral immunotherapy to highly peanut-allergic children ages 1 to 3 years safely desensitized most of them to peanut and induced remission of peanut allergy in one-fifth.


