Some of the health complications that arise from sexually transmitted infections (STIs) include pelvic inflammatory disease, infertility, tubal or ectopic pregnancy, cervical cancer, and perinatal or congenital infections in infants who have been exposed to STIs. Learn about the pathogens (infectious agents) and syndromes (conditions that develop due to infection and inflammation) for which NIAID supports research.
Bacterial Vaginosis
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) results from an imbalance in the vaginal microbiome (the mix of beneficial and harmful bacteria that are typically present in the vagina). BV occurs almost exclusively in people who are sexually active and can be caused by sexual activity or introducing other material in or near the vagina such as douches and menstrual products. BV can increase women’s biological susceptibility to HIV and other STIs and can cause premature birth or low birthweight if untreated in pregnant women.
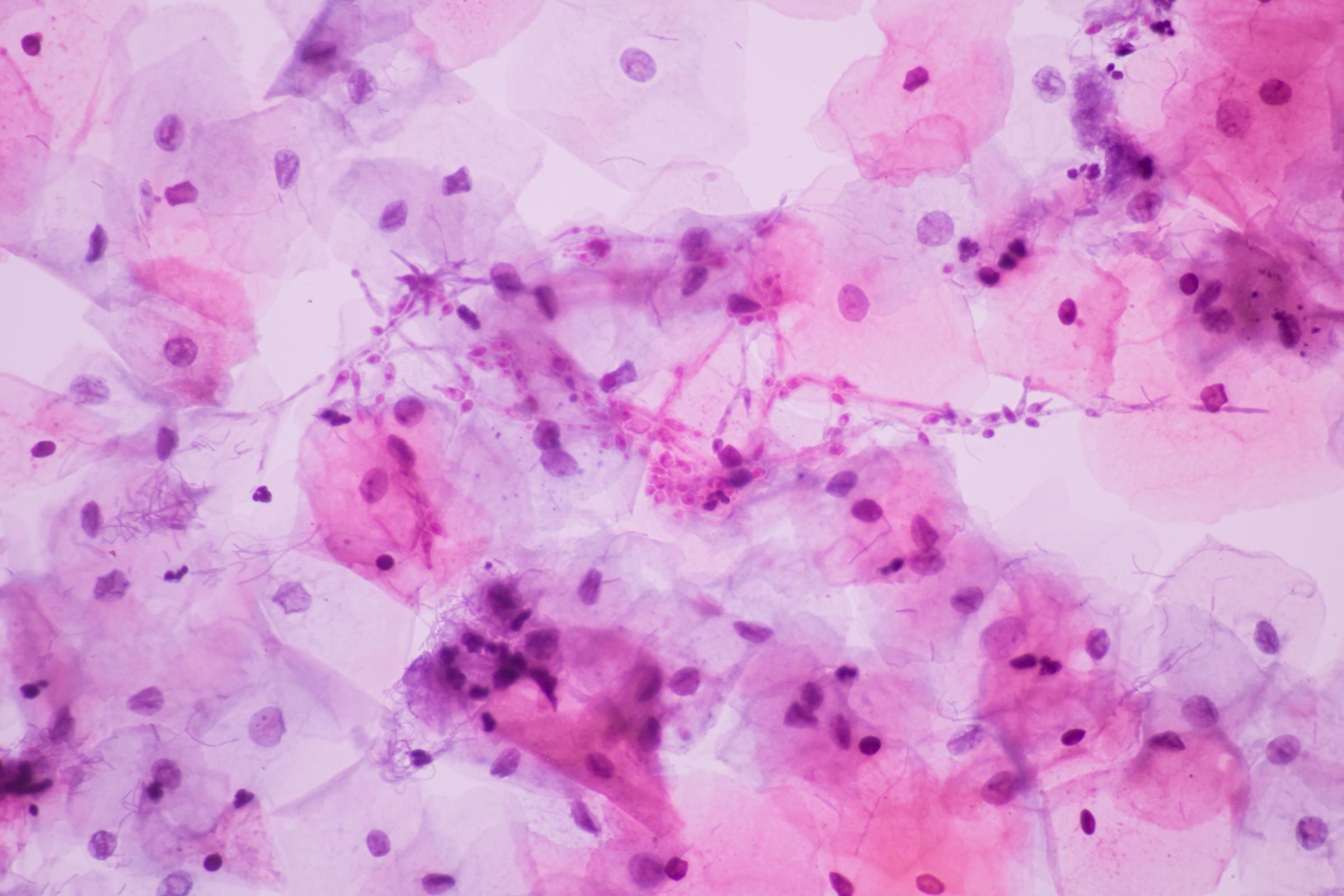
Candidiasis
Candida are yeast that can be found on the skin and in the intestinal tract, but also on mucosal surfaces such as the vagina. Candidiasis in the vagina is typically referred to as a “yeast infection.” Although there are more than 20 yeast that can cause candidiasis, the most common are Candida albicans, C. glabrata, C. parapsilosis and C. tropicalis.
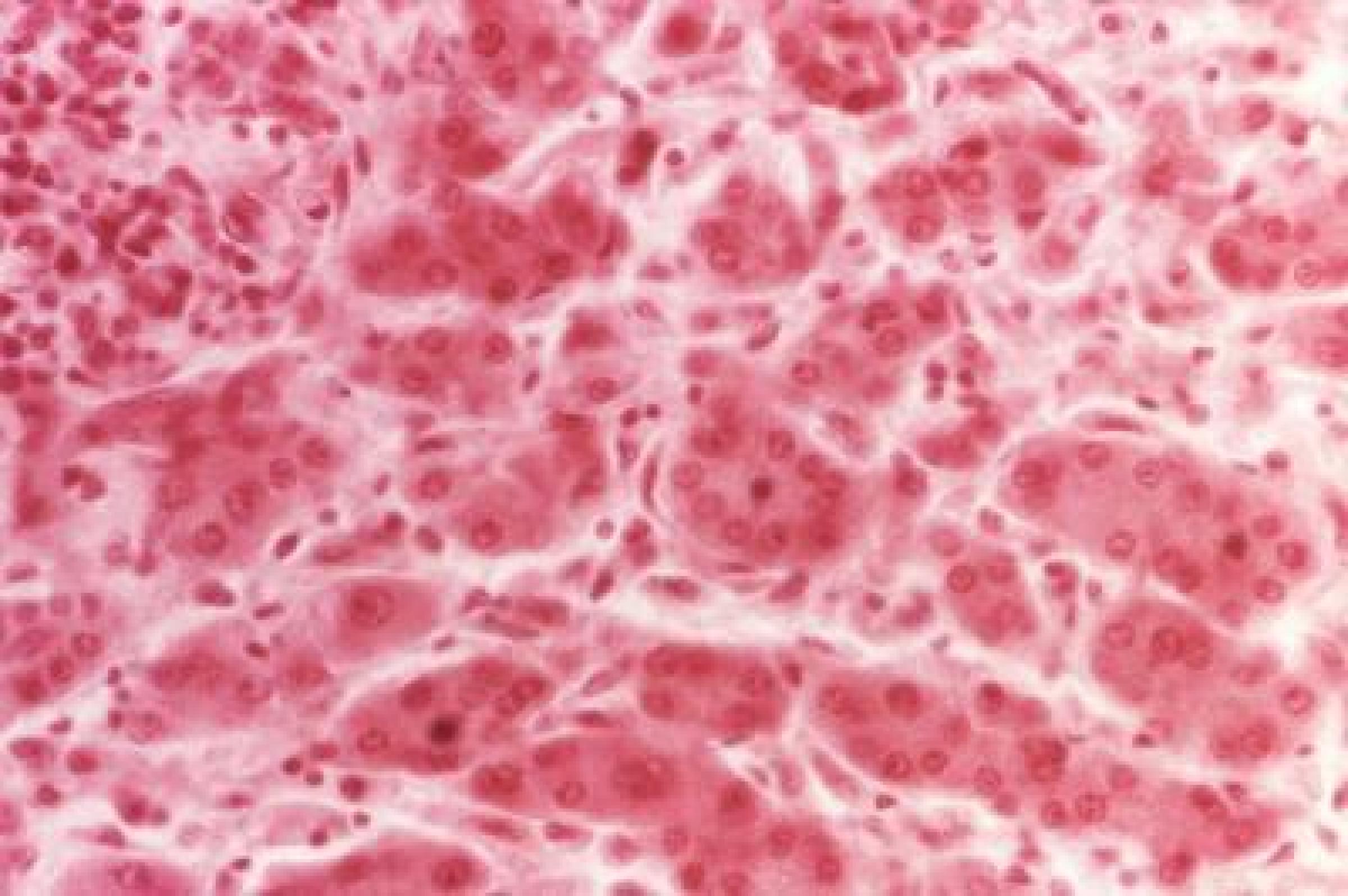
Chlamydia
Chlamydia is a common STI that can cause cervicitis in women and urethritis and proctitis in both men and women. NIAID and NIAID-supported researchers are studying how Chlamydia trachomatis bacteria causes disease and developing a vaccine to prevent C. trachomatis infection.
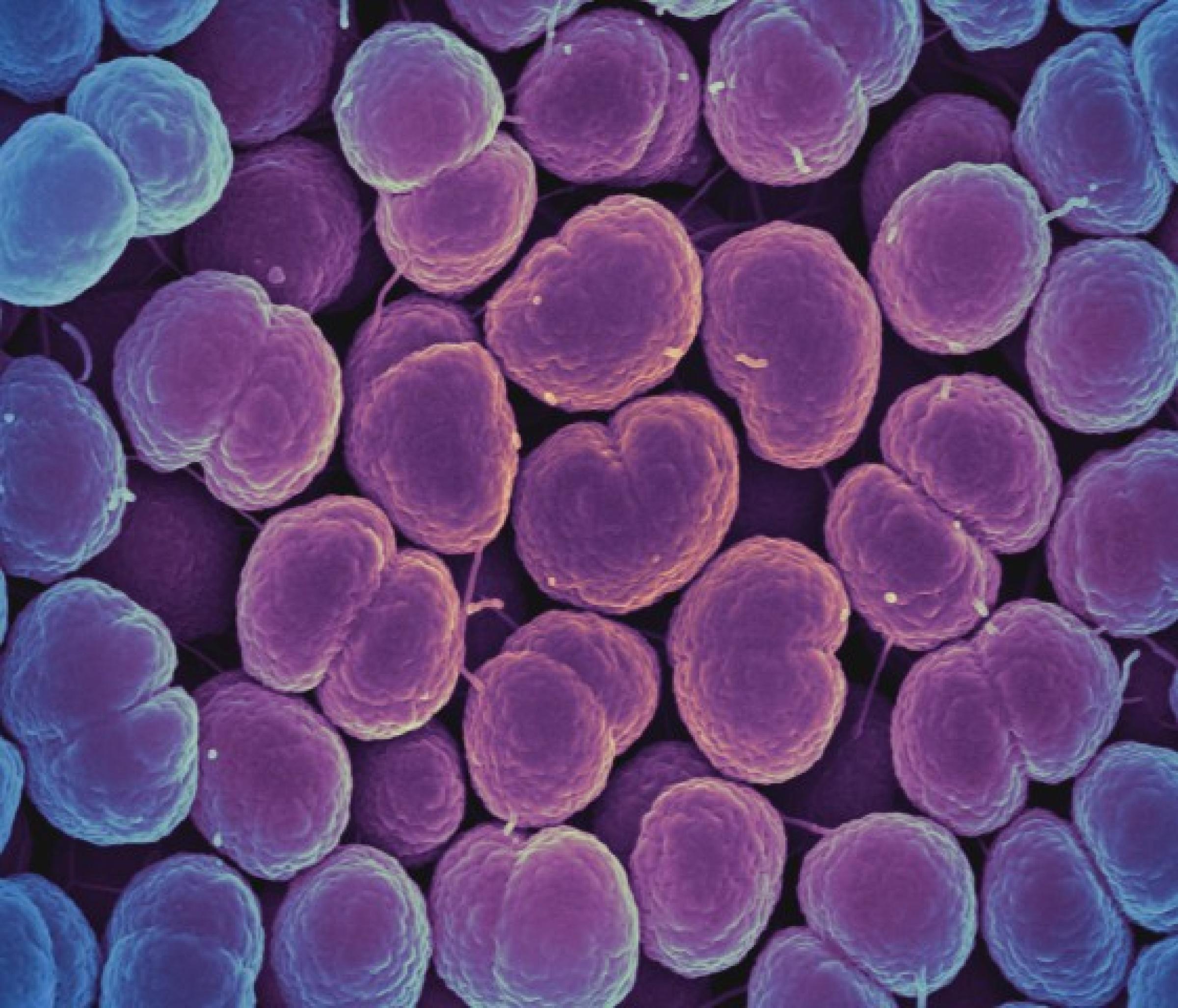
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is an STI caused by the bacteria Neisseria gonorrhoeae. N. gonorrhoeae infects the reproductive tract, including the cervix, uterus, and fallopian tubes in women, and the urethra in women and men. N. gonorrhoeae can also establish infection in the mouth, throat, eyes, and rectum.
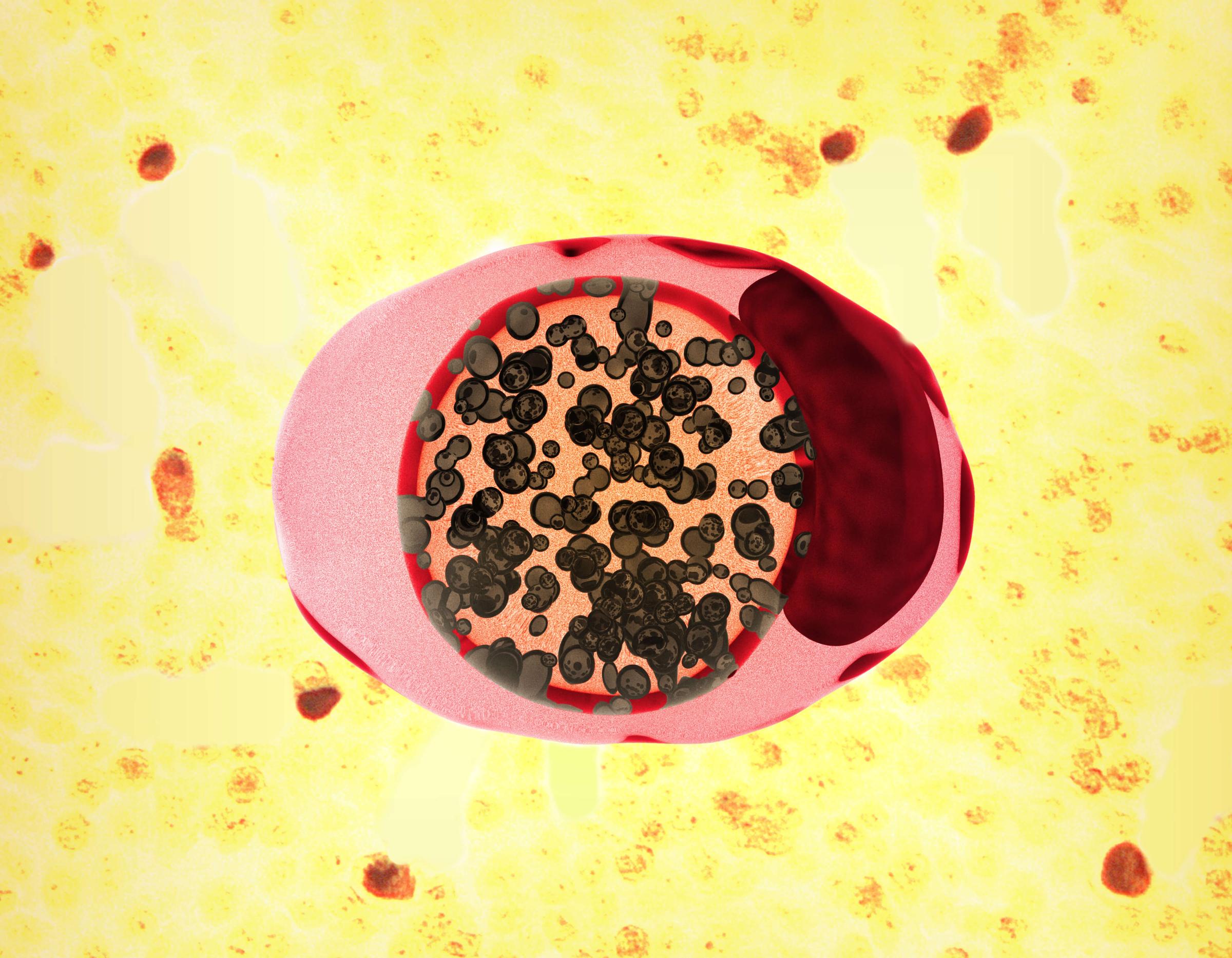
Hepatitis
Viral hepatitis is an inflammatory liver disease caused by infection with any of the known hepatitis viruses—A, B, C, D and E. Hepatitis B and C can be transmitted sexually and account for most of the global hepatitis burden.
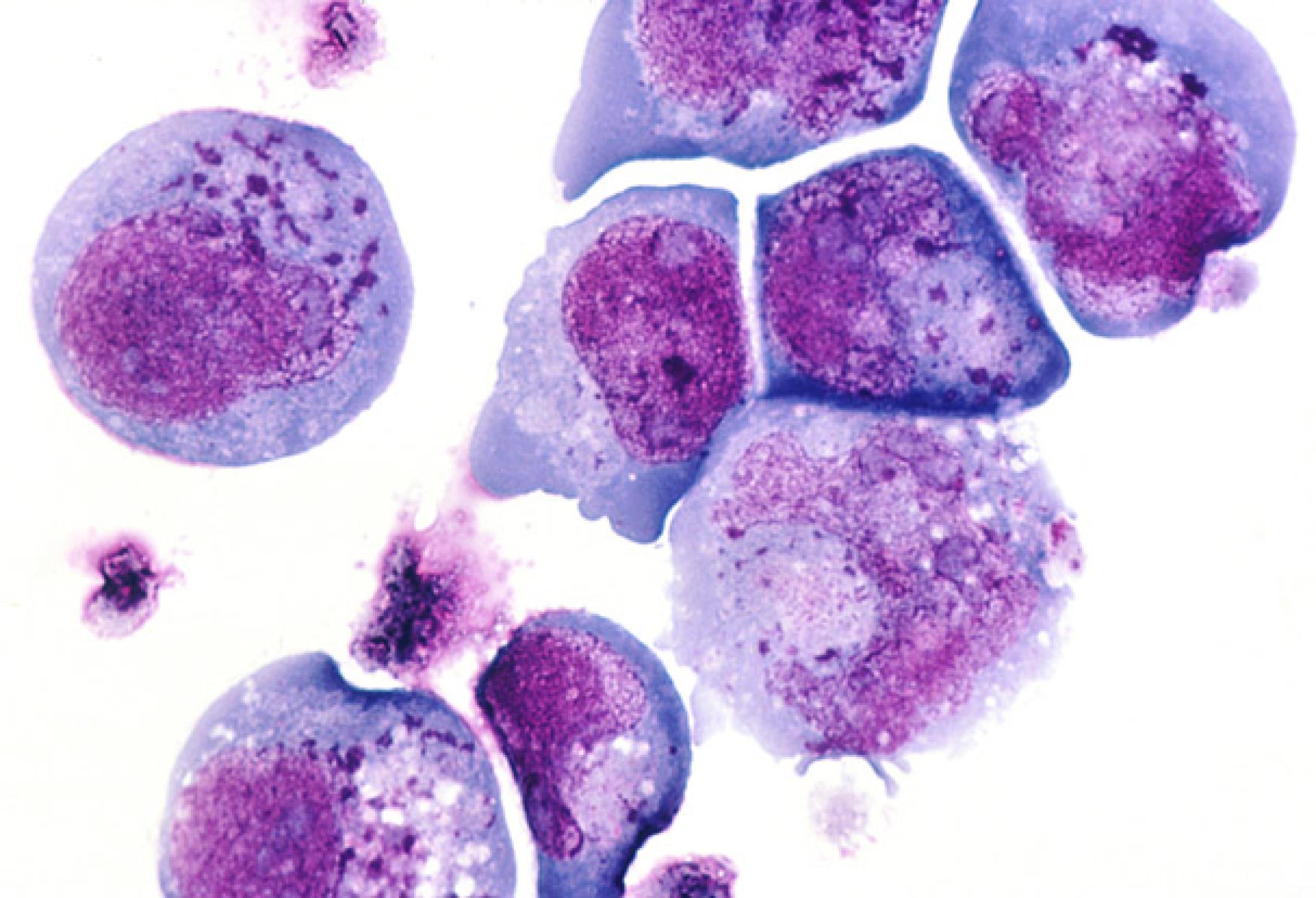
Herpes
Herpes, caused by herpes simplex virus (HSV), has two subtypes—HSV-1 and HSV-2. HSV can be transmitted through sexual contact. In severe cases HSV may lead to life-threatening or long-term complications, typically in the central nervous system. HSV is a leading cause of viral encephalitis—brain inflammation from a viral infection—and infectious blindness worldwide. Neonatal herpes, if left untreated, is fatal in 60% of cases.
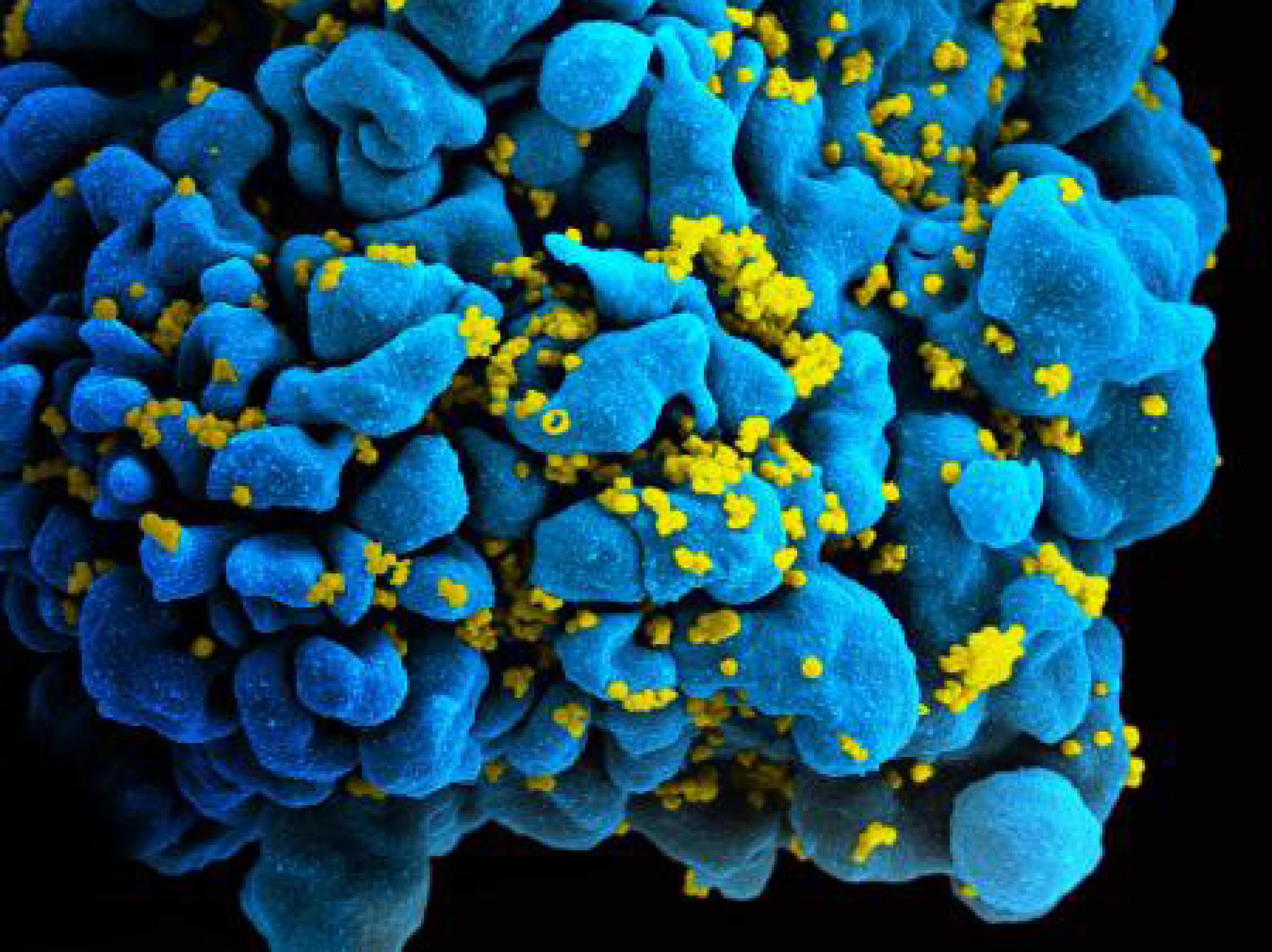
HIV
HIV, or human immunodeficiency virus, is the virus that causes acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). HIV attacks the immune system by entering and destroying CD4+ T cells, a type of white blood cell that is vital to fighting off infection. The destruction of these cells leaves people with HIV vulnerable to other pathogens and complications.
Human Papilloma Virus
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is the most common STI in the US, and often has no symptoms. Nearly all sexually active people get HPV at some point in their lives. There are many different types of HPV. Some types can cause health problems including genital warts and cancers. HPV causes about 5% of cancers worldwide, including cervical cancer and rising cases of oral, throat and anal cancers.
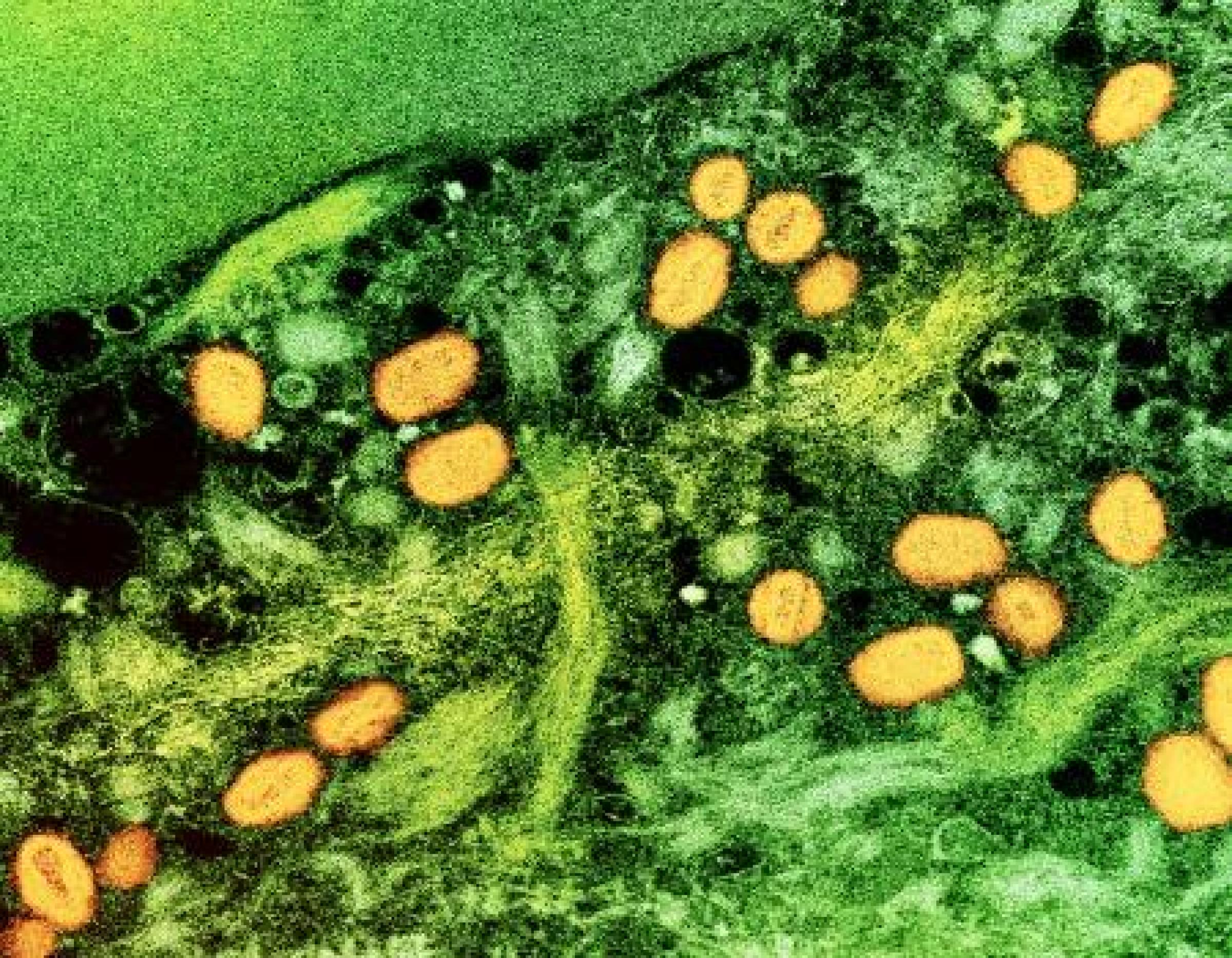
Mpox
The mpox virus has been endemic—occurring regularly—in west, central and east Africa since the first case of human mpox disease was identified in 1970. Mpox is spread through skin-to-skin contact, which can include sexual contact. People who acquire mpox tend to clear the infection on their own, but the virus can cause serious disease in children, pregnant women, and other people with compromised immune systems, including individuals with advanced HIV disease. Rare but serious complications of mpox include dehydration, bacterial infections, pneumonia, brain inflammation, sepsis, eye infections and death.
Mycoplasma genitalium
Mycoplasma genitalium is a significant cause of non-gonococcal urethritis and persistent urethritis in men, and is associated with cervicitis, pelvic inflammatory disease, preterm delivery, and infertility in women.
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is a general term that refers to infection and inflammation of the upper genital tract in women. It can affect the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and other organs related to reproduction. The scarring that results on these organs can lead to infertility, tubal (also known as “ectopic”) pregnancy, chronic pelvic pain, abscesses (sores), and other serious problems. PID is the most common preventable cause of infertility in the United States.
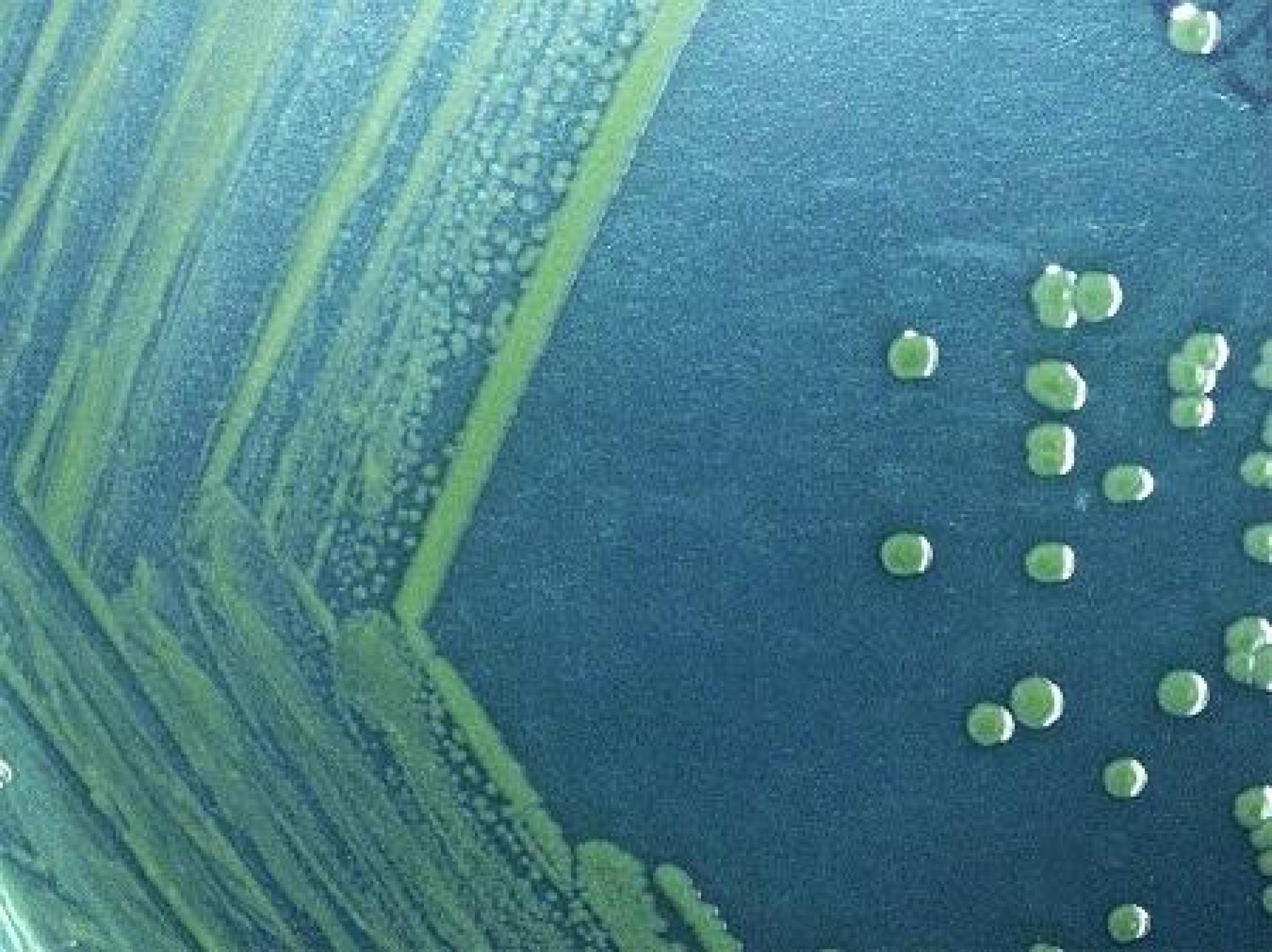
Shigellosis
Shigellosis is a diarrheal disease caused by infection with Shigella bacteria. Transmission of Shigella usually occurs through contact with the “4 Fs,” which are food, feces, flies, and fomites (inert surfaces). It also can also be spread through sexual contact.
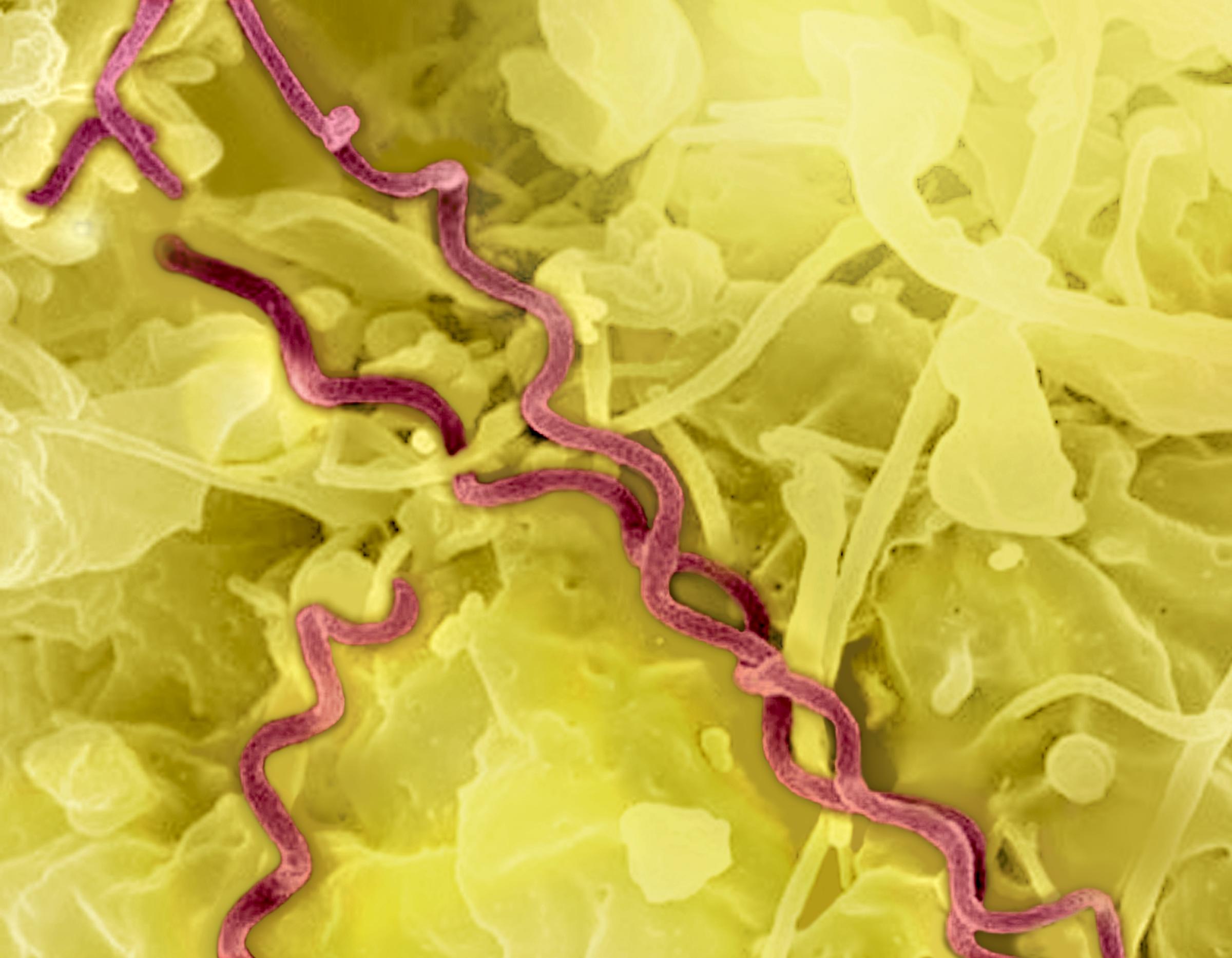
Syphilis
Syphilis is a common STI caused by Treponema pallidum bacteria. If untreated, syphilis can result in adult neurological and organ damage as well as congenital abnormalities, stillbirth, and neonatal death.
Trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis, is an infection caused by the Trichomonas vaginalis parasite. Trichomoniasis can increase the risk of getting or spreading other sexually transmitted infections.
Urethritis
Urethritis refers to infection and inflammation of the urethra. Urethritis is a condition that can result from infection with common STI pathogens including N. gonorrhoeae, C. trachomatis, T. vaginalis.


