Structural Informatics Unit
Audray K. Harris, Ph.D.
Chief, Structural Informatics Unit
Stadtman Investigator

Major Areas of Research
- Molecular architecture and assembly of viruses
- Structure-function and epitope mapping of viral glycoproteins
- Characterization and structural studies of vaccine immunogens and particles.
Program Description
Our research area is the structural biology of viruses and vaccine particles. One goal of the research is to understand the molecular organization of viruses in order to gain insights into virus assembly and function. Another goal is to study the organization of conserved viral epitopes on vaccine particles to help inform vaccine development. The research program exploits 3D electron microscopy of viruses and protein complexes with antibodies to obtain structural information on epitope disposition and conformational states. Structural analyses are supported by other structural, biochemical, and immunological analyses in order to understand immunogenicity, antigen-antibody interactions and aid in structure-assisted design of nanoparticles for vaccines. A major focus is on the structure, assembly, and epitope display of influenza proteins and viral particles.
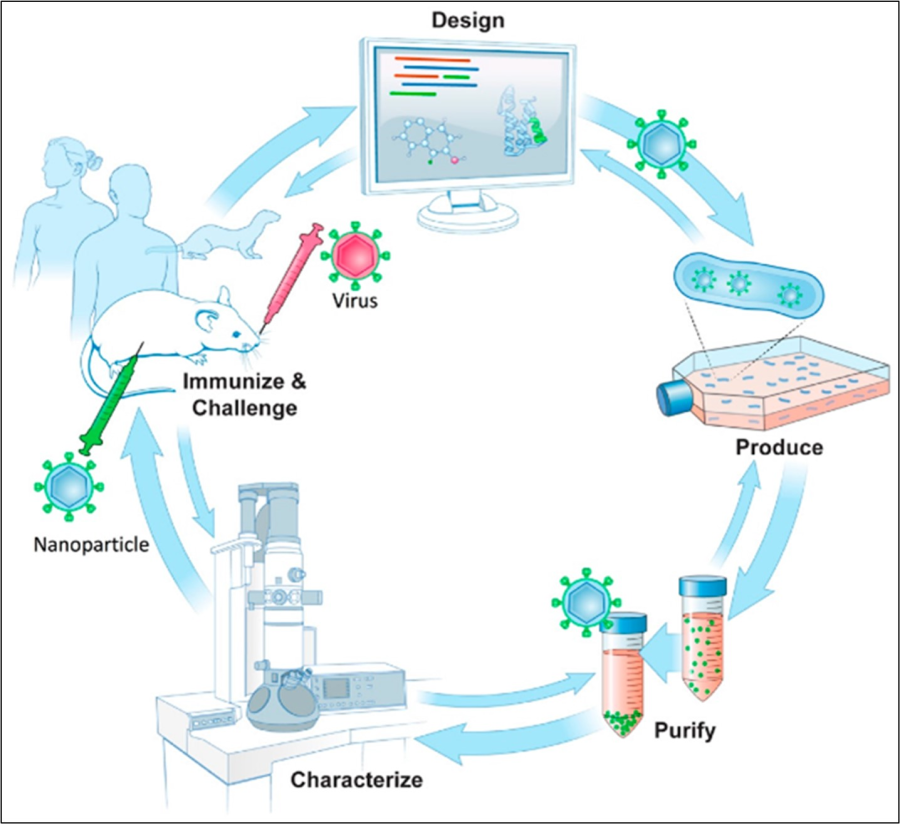
Schematic of structure-guided immunogen design integrated into a vaccine development pipeline. (Design) A conserved epitope from a surface antigen (green) is designed into a fusion protein in order for epitope display on a nanoparticle. Design uses bioinformatics taking into account conserved sequences and epitopes along with structural and molecular modeling of nanoparticle structures in silico. (Produce) To produce nanoparticles, protein encoding DNAs are synthesized and screened for protein expression and nanoparticle formation. (Purify) Nanoparticle production and purification is scaled for further characterization. (Characterize) Immunoassays and biophysical techniques such as electron microscopy are used. 3D structures can be produced by cryo-EM to assess particle integrity, along with epitope display and conformation. (Immunize, Challenge) Immunogenicity and challenge studies using nanoparticles as immunogens can be carried out in animal models, such as mice and ferrets with progression into human studies. Double arrows denote the general iterative nature among steps in the process of structure-guided antigen design within a vaccine pipeline.
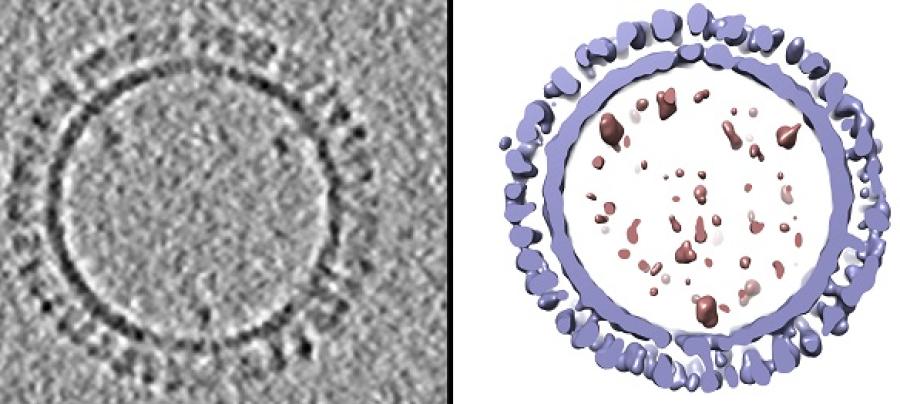
Caption:
On the left is a 1918 H1 influenza virus-like particle (VLP) as seen by cryo-electron microscopy. On the right is the same VLP rendered in 3D with structural components computationally segmented and colored; hemagglutinin and membrane are light blue and internal components (molecular cargo) are red.
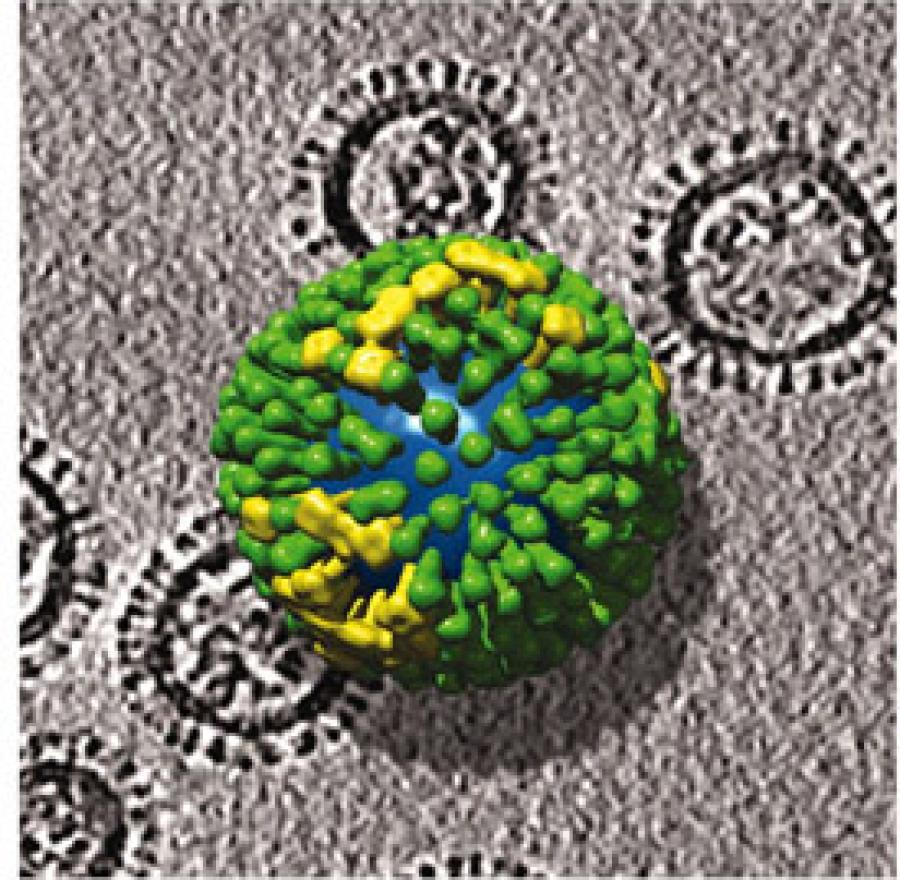
Influenza virus particles.
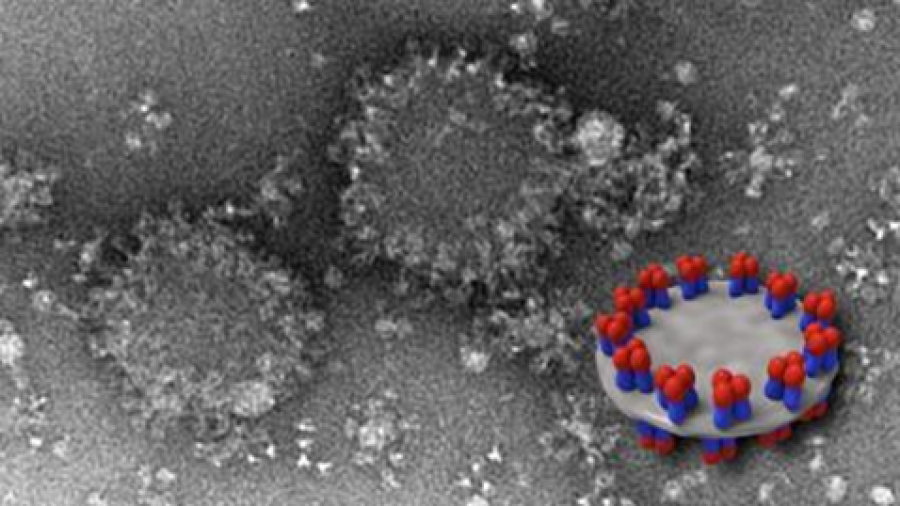
EM image of spiked nanodisc structures (background) with a schematic model (foreground) showing HA complexes arranged on edge.
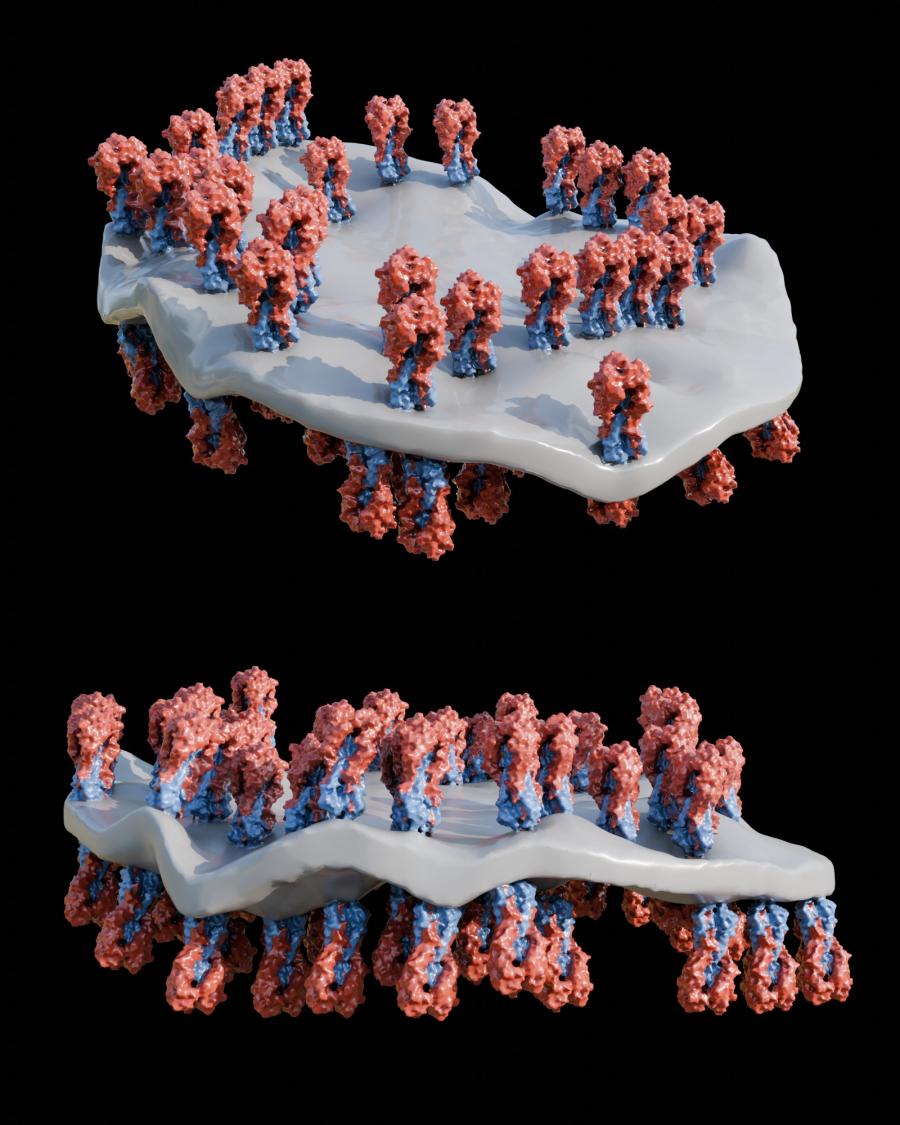
Using cryo-electron tomography, the laboratory of Audray K. Harris identified a novel structural display of hemagglutinin (HA). By utilizing this unique presentation of HA along the peripheral edge of a lipid membrane, this vaccine elicits more antibodies to conserved HA regions compared to other vaccine structures studied.
Biography
Education
Ph.D., 2002, The University of Alabama at Birmingham
Dr. Harris received his Ph.D. in 2002 from The University of Alabama at Birmingham. Following postdoctoral training at the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, he joined the National Cancer Institute as a research fellow. In 2012, Dr. Harris was selected as an Earl Stadtman Investigator and in 2013 joined the Laboratory of Infectious Diseases.
Selected Publications
McCraw DM, Myers ML, Gulati NM, Prabhakaran M, Brand J, Andrews S, Gallagher JR, Maldonado-Puga S, Kim AJ, Torian U, Syeda H, Boyoglu-Barnum S, Kanekiyo M, McDermott AB, Harris AK. Designed nanoparticles elicit cross-reactive antibody responses to conserved influenza virus hemagglutinin stem epitopes. PLoS Pathog. 2023 Aug 28;19(8):e1011514.
Myers ML, Gallagher JR, Kim AJ, Payne WH, Maldonado-Puga S, Assimakopoulos H, Bock KW, Torian U, Moore IN, Harris AK. Commercial influenza vaccines vary in HA-complex structure and in induction of cross-reactive HA antibodies. Nat Commun. 2023 Mar 30;14(1):1763.
Myers ML, Gallagher JR, Woolfork DD, Stradtmann-Carvalho RK, Maldonado-Puga S, Bock KW, Boyoglu-Barnum S, Syeda H, Creanga A, Alves DA, Kanekiyo M, Harris AK. Impact of adjuvant: Trivalent vaccine with quadrivalent-like protection against heterologous Yamagata-lineage influenza B virus. Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 30;13:1002286.
Moin SM, Boyington JC, Boyoglu-Barnum S, Gillespie RA, Cerutti G, Cheung CS, Cagigi A, Gallagher JR, Brand J, Prabhakaran M, Tsybovsky Y, Stephens T, Fisher BE, Creanga A, Ataca S, Rawi R, Corbett KS, Crank MC, Karlsson Hedestam GB, Gorman J, McDermott AB, Harris AK, Zhou T, Kwong PD, Shapiro L, Mascola JR, Graham BS, Kanekiyo M. Co-immunization with hemagglutinin stem immunogens elicits cross-group neutralizing antibodies and broad protection against influenza A viruses. Immunity. 2022 Dec 13;55(12):2405-2418.e7.
Kanekiyo M, Joyce MG, Gillespie RA, Gallagher JR, Andrews SF, Yassine HM, Wheatley AK, Fisher BE, Ambrozak DR, Creanga A, Leung K, Yang ES, Boyoglu-Barnum S, Georgiev IS, Tsybovsky Y, Prabhakaran MS, Andersen H, Kong WP, Baxa U, Zephir KL, Ledgerwood JE, Koup RA, Kwong PD, Harris AK, McDermott AB, Mascola JR, Graham BS. Mosaic nanoparticle display of diverse influenza virus hemagglutinins elicits broad B cell responses. Nat Immunol. 2019 Mar;20(3):362-372.
Dowd KA, Ko SY, Morabito KM, Yang ES, Pelc RS, DeMaso CR, Castilho LR, Abbink P, Boyd M, Nityanandam R, Gordon DN, Gallagher JR, Chen X, Todd JP, Tsybovsky Y, Harris A, Huang YS, Higgs S, Vanlandingham DL, Andersen H, Lewis MG, De La Barrera R, Eckels KH, Jarman RG, Nason MC, Barouch DH, Roederer M, Kong WP, Mascola JR, Pierson TC, Graham BS. Rapid development of a DNA vaccine for Zika virus. Science. 2016 Oct 14;354(6309):237-240.
Articles
Close-up view of protein-complex structures could lead to better flu vaccines
Research Group
John Gallagher, Mallory Myers Iosefson, Samantha Maldonado Puga, Crisinta Corsino, De’Marcus Woolfork, Noah Khorrami, William Park

